Gut Bacteria Shared by Children and Their Mothers Associate with Developmental Level and Social Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 33268567
- PMCID: PMC7716279
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.01044-20
Gut Bacteria Shared by Children and Their Mothers Associate with Developmental Level and Social Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
The gut microbiota of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) children differs from that of children without ASD. The maternal gut microbiota impacts offspring gut microbiota. However, the relationship between the development of ASD and gut bacteria shared between children and their mothers remains elusive. Our study recruited 76 children with ASD and 47 age- and gender-matched children with typical development (TD), as well as the mothers of both groups, and investigated their gut microbiota using amplicon sequence variants (ASVs). The gut microbiota of ASD children was altered compared with that of children with TD, while no significant alterations were found in their mothers. We established 30 gut bacterial coabundance groups (CAGs) and found the relative abundances of CAG15 and CAG16 significantly decreased in ASD children. CAG15 showed a positive correlation with developmental level. The proportion of ASD children who shared either one of the two Lachnospiraceae ASVs from CAG15 with their mothers was significantly lower than that of children with TD. Moreover, we found that CAG12, CAG13, and CAG18 negatively correlated with the severity of social deficits in ASD children. ASD children who shared any one of the four (two Ruminococcaceae, one Lachnospiraceae, and one Collinsella) ASVs in CAG13 and CAG18 with their mothers showed a lower level of social deficits than ASD children that did not share those with their mothers. These data demonstrate that these shared gut bacteria in ASD children are associated with their developmental level and social deficits. This work provides a new direction toward understanding the role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and development of ASD. (This study has been registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry under number ChiCTR-RPC-16008139.)IMPORTANCE Gut microbiota may contribute to the pathogenesis and development of autism spectrum disorder. The maternal gut microbiota influences offspring gut microbial structure and composition. However, the relationship between the clinical symptoms of autism spectrum disorder and the gut bacteria shared between children and their mothers is not yet known. In our study, the gut microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorder differed from that of children with typical development, but there were no differences in the gut microbiota of their mothers. More importantly, gut bacteria shared between children with autism spectrum disorder and their mothers were related to developmental disabilities and social deficits. Thus, our study suggests that these shared gut bacteria may play an important role in the development of autism spectrum disorder. This provides a new direction for future studies aiming to explore the role of the gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorder.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; developmental level; gut microbiota; mother-child pair; social deficits.
Copyright © 2020 Chen et al.
Figures
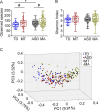

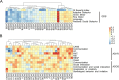
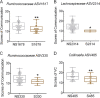
References
-
- Maenner MJ, Shaw KA, Baio J, Washington A, Patrick M, DiRienzo M, Christensen DL, Wiggins LD, Pettygrove S, Andrews JG, Lopez M, Hudson A, Baroud T, Schwenk Y, White T, Rosenberg CR, Lee L-C, Harrington RA, Huston M, Hewitt A, Esler A, Hall-Lande J, Poynter JN, Hallas-Muchow L, Constantino JN, Fitzgerald RT, Zahorodny W, Shenouda J, Daniels JL, Warren Z, Vehorn A, Salinas A, Durkin MS, Dietz PM, PhD-7. 2020. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill Summ 69:1–12. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6904a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
