Pathological Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Review
- PMID: 33269111
- PMCID: PMC7673851
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2020.0111
Pathological Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Review
Abstract
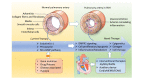
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a progressive cardiovascular disease characterized by pulmonary vasculature reconstruction and right ventricular dysfunction. The mortality rate of PAH remains high, although multiple therapeutic strategies have been implemented in clinical practice. These drugs mainly target the endothelin-1, prostacyclin and nitric oxide pathways. Management for PAH treatment includes improving symptoms, enhancing quality of life, and extending survival rate. Existing drugs developed to treat the disease have resulted in enormous economic and healthcare liabilities. The estimated cost for advanced PAH has exceeded $200,000 per year. The pathogenesis of PAH is associated with numerous molecular processes. It mainly includes germline mutation, inflammation, dysfunction of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells, epigenetic modifications, DNA damage, metabolic dysfunction, sex hormone imbalance, and oxidative stress, among others. Findings based on the pathobiology of PAH may have promising therapeutic outcomes. Hence, faced with the challenges of increasing healthcare demands, in this review, we attempted to explore the pathological mechanisms and alternative therapeutic targets, including other auxiliary devices or interventional therapies, in PAH. The article will discuss the potential therapies of PAH in detail, which may require further investigation before implementation.
Keywords: hemodynamics; pulmonary arterial hypertension; right ventricular dysfunction; therapy advances.
copyright: © 2020 Xiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. (2015). 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Respir J, 46:903-975. - PubMed
-
- Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, et al. (2013). Updated Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 62:D34-D41. - PubMed
-
- Condliffe R, Kiely DG, Peacock AJ, Corris PA, Gibbs JS, Vrapi F, et al. (2009). Connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern treatment era. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 179:151-157. - PubMed
-
- Peacock AJ, Murphy NF, McMurray JJ, Caballero L, Stewart S (2007). An epidemiological study of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J, 30:104-109. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
