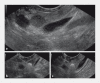
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a case series
- PMID: 33269307
- PMCID: PMC7671764
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1261-9359
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a case series
Abstract
Background and study aims Surgery is the considered the therapeutic cornerstone for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (P-NETs), although burdened by high risk of significant adverse events. Recently, endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) has been described for P-NETs. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of EUS-RFA for treatment of P-NETs. Patients and methods We prospectively included all consecutive patients with P-NET ≤ 20 mm who were treated with EUS-RFA and were followed-up for at least 12 months. Results Ten patients (5 males, mean age 78.6 years, mean body mass index 28.2) with 11 P-NETs (mean size 14.5 mm; range 9 - 20 mm) localized in the pancreatic head (3 lesions), pancreatic body (5 lesions), and tail (3 lesions) underwent complete EUS ablation with one session of RFA. Complete ablation of P-NET was reached using a single-session RFA with a mean of 2.3 treatment applications per session. At both 6 - and 12-months computed tomography scans, all the patients had complete disappearance of lesions with radiological normalization. Regarding safety, only two cases of mild abdominal pain were recorded in two subjects with pancreatic head lesion, which were effectively treated with analgesics. The mean duration of hospital stay was 4 days (range 3 - 7 days). Conclusions EUS-RFA is effective and safe in treating P-NETs. It may be considered an effective therapeutic option in the treatment of small P-NETs independently from their functional status.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commecial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzgerald T L, Hickner Z J, Schmitz M et al.Changing incidence of pancreatic neoplasms: a 16-year review of statewide tumor registry. Pancreas. 2008;37:134–138. - PubMed
-
- Sachs T, Pratt W B, Callery M P et al.The incidental asymptomatic pancreatic lesion: nuisance or treat? J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:405–415. - PubMed
-
- Rossi S, Viera F T, Ghittoni G et al.Radiofrequency ablation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a pilot study of feasibility, efficacy, and safety. Pancreas. 2014;43:938–945. - PubMed
-
- Armellini E, Crinò S F, Ballarè M et al.Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Endoscopy. 2015 01:47. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources