The SARS-COV-2 Spike Protein Binds Sialic Acids and Enables Rapid Detection in a Lateral Flow Point of Care Diagnostic Device
- PMID: 33269329
- PMCID: PMC7523238
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00855
The SARS-COV-2 Spike Protein Binds Sialic Acids and Enables Rapid Detection in a Lateral Flow Point of Care Diagnostic Device
Erratum in
-
Correction to "The SARS-COV-2 Spike Protein Binds Sialic Acids, and Enables Rapid Detection in a Lateral Flow Point of Care Diagnostic Device".ACS Cent Sci. 2021 Feb 24;7(2):379-380. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00027. Epub 2021 Jan 14. ACS Cent Sci. 2021. PMID: 33655075 Free PMC article.
Abstract
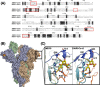
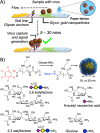
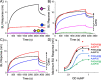
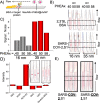
There is an urgent need to understand the behavior of the novel coronavirus (SARS-COV-2), which is the causative agent of COVID-19, and to develop point-of-care diagnostics. Here, a glyconanoparticle platform is used to discover that N-acetyl neuraminic acid has affinity toward the SARS-COV-2 spike glycoprotein, demonstrating its glycan-binding function. Optimization of the particle size and coating enabled detection of the spike glycoprotein in lateral flow and showed selectivity over the SARS-COV-1 spike protein. Using a virus-like particle and a pseudotyped lentivirus model, paper-based lateral flow detection was demonstrated in under 30 min, showing the potential of this system as a low-cost detection platform.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): M.I.G., A.N.B., and S.J.R. are named inventors of a patent relating to this work. R.F. is a shareholder in Iceni diagnostics who part-funded this work.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou P.; Yang X.-L.; Wang X.-G.; Hu B.; Zhang L.; Zhang W.; Si H.-R.; Zhu Y.; Li B.; Huang C.-L.; Chen H.-D.; Chen J.; Luo Y.; Guo H.; Jiang R.-D.; Liu M.-Q.; Chen Y.; Shen X.-R.; Wang X.; Zheng X.-S.; Zhao K.; Chen Q.-J.; Deng F.; Liu L.-L.; Yan B.; Zhan F.-X.; Wang Y.-Y.; Xiao G.-F.; Shi Z.-L. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579 (7798), 270–273. 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

