This is a preprint.
Timing the SARS-CoV-2 Index Case in Hubei Province
- PMID: 33269353
- PMCID: PMC7709179
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.11.20.392126
Timing the SARS-CoV-2 Index Case in Hubei Province
Update in
-
Timing the SARS-CoV-2 index case in Hubei province.Science. 2021 Apr 23;372(6540):412-417. doi: 10.1126/science.abf8003. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Science. 2021. PMID: 33737402 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Understanding when SARS-CoV-2 emerged is critical to evaluating our current approach to monitoring novel zoonotic pathogens and understanding the failure of early containment and mitigation efforts for COVID-19. We employed a coalescent framework to combine retrospective molecular clock inference with forward epidemiological simulations to determine how long SARS-CoV-2 could have circulated prior to the time of the most recent common ancestor. Our results define the period between mid-October and mid-November 2019 as the plausible interval when the first case of SARS-CoV-2 emerged in Hubei province. By characterizing the likely dynamics of the virus before it was discovered, we show that over two-thirds of SARS-CoV-2-like zoonotic events would be self-limited, dying out without igniting a pandemic. Our findings highlight the shortcomings of zoonosis surveillance approaches for detecting highly contagious pathogens with moderate mortality rates.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: JOW has received funding from Gilead Sciences, LLC (completed) and the CDC (ongoing) via grants and contracts to his institution unrelated to this research.
Figures


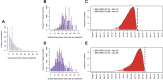
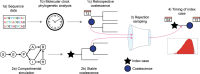

References
-
- Li Q., Guan X., Wu P., Wang X., Zhou L., Tong Y., Ren R., Leung K. S. M., Lau E. H. Y., Wong J. Y., Xing X., Xiang N., Wu Y., Li C., Chen Q., Li D., Liu T., Zhao J., Liu M., Tu W., Chen C., Jin L., Yang R., Wang Q., Zhou S., Wang R., Liu H., Luo Y., Liu Y., Shao G., Li H., Tao Z., Yang Y., Deng Z., Liu B., Ma Z., Zhang Y., Shi G., Lam T. T. Y., Wu J. T., Gao G. F., Cowling B. J., Yang B., Leung G. M., Feng Z., Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. (2020), doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), (available at https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/report-of-the-who-china...).
-
- WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020, (available at https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera...).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
