CTRP3 and serum triglycerides in children aged 7-10 years
- PMID: 33270666
- PMCID: PMC7714231
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241813
CTRP3 and serum triglycerides in children aged 7-10 years
Abstract
Introduction: The prevalence of obesity-related disorders has been steadily increasing over the past couple of decades. Diseases that were once only detected in adults are now prevalent in children, such as hyperlipidemia. The adipose tissue-derived hormonal factor C1q TNF Related Protein 3 (CTRP3) has been linked to triglyceride regulation especially in animal models. However, the relationship between circulating CTRP3 levels and obesity-related disorders in human subjects is controversial. CTRP3 can circulate in different oligomeric complexes: trimeric (<100 kDa), middle molecular weight (100-300 kDa), and high molecular weight (HMW) oligomeric complexes (>300 kDa). Previous work has identified that it is not the total amount of CTRP3 present in the serum, but the specific circulating oligomeric complexes that appear to be indicative of the relationship between CTRP3 and serum lipids levels. However, this work has not been examined in children. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare the levels of different oligomeric complexes of CTRP3 and circulating lipid levels among young children (aged 7-10 years).
Methods: Morphometric data and serum samples were collected and analyzed from a cross-sectional population of 62 children of self-identified Hispanic origin from a community health center, between 2015 and 2016. Serum analysis included adiponectin, insulin, leptin, ghrelin, glucagon, C-reactive peptide, triglyceride, cholesterol, IL-6, TNF, and CTRP3. Correlation analyses were conducted to explore the relationships between CTRP3 and other biomarkers.
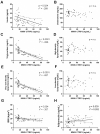
Results: Total CTRP3 concentrations were significantly positively correlated with total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol. Whereas, HMW CTRP3 was not significantly associated with any variable measured. Conversely, the middle molecular weight (MMW) CTRP3 was negatively correlated with triglycerides levels, and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), insulin, and body mass index (BMI). The negative correlations between MMW CTRP3 and triglycerides and VLDLs were particularly strong (r2 = -0.826 and -0.827, respectively).
Conclusion: Overall, these data indicate that the circulating oligomeric state of CTRP3 and not just total CTRP3 level is important for understanding the association between CTRP3 and metabolic diseases. Further, this work indicates that MMW CTRP3 plays an important role in triglyceride and VLDL regulation which requires further study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Troiano RP, Flegal KM. Overweight children and adolescents: description, epidemiology, and demographics. Pediatrics. 1998;101(3 Pt 2):497–504. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

