Changes in corneal astigmatism and near heterophoria after smartphone use while walking and sitting
- PMID: 33270709
- PMCID: PMC7714198
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243072
Changes in corneal astigmatism and near heterophoria after smartphone use while walking and sitting
Abstract
Background/aims: Smartphone use has become an indispensable part of our daily life. The handy design and powerful processor allow smartphone users to perform diversified tasks even when walking. This study aimed to investigate and compare the optical aftereffect and vergence adaptation of using a smartphone while walking and sitting.
Methods: Twenty-nine young healthy adults (aged 19 to 24 years old) with normal binocular and accommodative functions were recruited. Participants were asked to watch a movie for 30 minutes using a smartphone while either walking on a treadmill or sitting on a chair. Corneal aberrations and near heterophoria were measured before and after smartphone use by a corneal topographer and modified Thorington heterophoria test, respectively.
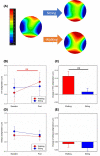
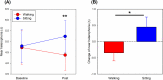
Results: Using the smartphone while walking induced a change in corneal H/V astigmatism, becoming 0.11±0.03 μm less negative (two-way ANOVA repeated measures, Bonferroni post-hoc test, p = 0.001). This optical aftereffect was significantly higher than after smartphone use while sitting by 0.10±0.03 μm (paired t-test, p = 0.003). Although smartphone use did not result in a significant change in near heterophoria (Bonferroni post-hoc test, p > 0.15), the vergence adaptation showed relatively more eso- or less exo-deviation by 0.79±0.36Δ in the walking than the sitting condition (paired t-test, p = 0.037).
Conclusions: Eyecare practitioners should be cautious of the potential optical after effect and vergence adaptation after prolonged smartphone usage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- O'Dea S. Smartphone users worldwide 2016–2021. 2020. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/330695/number-of-smartphone-users-wo....
-
- Census and Statistics Department Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Information technology usage and penetration. In: Census and Statistics Department, editor. Hong Kong 2018.
-
- Chung R. Modern Family Lifestyle Survey2013. Available from: https://www.hkupop.hku.hk/english/report/modernFamilyLifestyle/content/r....
-
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Distracted Walking Study. 2015. Available from: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00748.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

