Multi-stakeholder consensus on a target product profile for an HIV cure
- PMID: 33271125
- PMCID: PMC7773628
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30234-4
Multi-stakeholder consensus on a target product profile for an HIV cure
Abstract
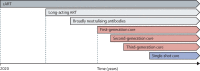
Developing a cure for HIV is a global priority. Target product profiles are a tool commonly used throughout the drug development process to align interested parties around a clear set of goals or requirements for a potential product. Three distinct therapeutic modalities (combination therapies, ex-vivo gene therapy, and in-vivo gene therapy) for a target product profile for an HIV cure were identified. Using a process of expert face-to-face consultation and an online Delphi consultation, we found a high degree of agreement regarding the criteria for the optimum target product profile. Although the minimum attributes for a cure were debated, the broad consensus was that an acceptable cure need not be as safe and effective as optimally delivered antiretroviral therapy. An intervention that successfully cured a reasonable fraction of adults would be sufficient to advance to the clinic. These target product profiles will require further discussion and ongoing revisions as the field matures.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- United Nations Joint Programme on HIV/AIDS AIDSinfo. 2020. http://aidsinfo.unaids.org
-
- Frank TD, Carter A, Jahagirdar D. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and mortality of HIV, 1980–2017, and forecasts to 2030, for 195 countries and territories: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017. Lancet HIV. 2019;6:e831–e859. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collier DA, Monit C, Gupta RK. The impact of HIV-1 drug escape on the global treatment landscape. Cell Host Microbe. 2019;26:48–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

