Rose Hips, a Valuable Source of Antioxidants to Improve Gingerbread Characteristics
- PMID: 33271766
- PMCID: PMC7731331
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25235659
Rose Hips, a Valuable Source of Antioxidants to Improve Gingerbread Characteristics
Abstract
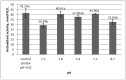
The present study analyzes the complex of bioactive compounds from rose hips pulp powder (RHP) obtained after separating the seeds from Rosa canina L. in order to obtain the oil. The extract prepared from RHP was characterized in terms of the total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, cinnamic acids, flavonols, carotenoids, but also the content of individual polyphenols and carotenoids, antioxidant activity, and CIELab color parameters. The effects of some salts, potentially present in foods, and pH variations were examined to predict possible interactions that could occur when adding rosehip pulp as a food component. The results turned out to be a high content of polyphenols, carotenoids and antioxidant activity. The main phenolic components are procyanidin B1, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, procyanidin B2, gallic acid, salicylic acid, and catechin. The carotenoid complex includes all-trans-β-carotene, all-trans-lycopene, zeaxanthin, α-cryptoxanthin, β-cryptoxanthin, rubixanthin, cis-β-carotene, cis-γ-carotene and cis-lycopene. The addition of CaCl2 and NaCl to the RHP extract reduced the antioxidant activity and the strong acidic environment (pH to 2.5) decreased the antioxidant activity by 29%. The addition of rose hip powder to gingerbread has improved its general characteristics, and increased its antioxidant activity and microbiological stability, the effects of 4% RHP being the most important.
Keywords: Rosa canina L.; antioxidant activity; bioactive compounds; carotenoids; food; natural compounds; phenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Scott-Thomas C. Natural and Organic Trends Drive European Food Colourings Growth. [(accessed on 15 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.confectionerynews.com/Article/2014/10/08/Natural-and-organic....
-
- Watson E. Kalsec: In Europe, Natural Food Colors Are Now ‘Standard Operating Procedure’, in the US Companies Are Just Starting to Look at Them. [(accessed on 1 November 2020)]; Available online: http://www.foodnavigator-usa.com/
-
- Patel S. Rose hips as complementary and alternative medicine: Overview of the present status and prospects. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012 doi: 10.3233/s12349-012-0118-7. - DOI
-
- Yildiz O., Alpaslan M. Rose hip marmalade. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2012;50:98–106.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

