Targeting HGF/c-MET Axis in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 33271944
- PMCID: PMC7730415
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21239170
Targeting HGF/c-MET Axis in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
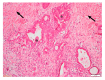
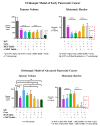
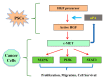
Pancreatic cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC/PC)) has been an aggressive disease that is associated with early metastases. It is characterized by dense and collagenous desmoplasia/stroma, predominantly produced by pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs). PSCs interact with cancer cells as well as other stromal cells, facilitating disease progression. A candidate growth factor pathway that may mediate this interaction is the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-MET pathway. HGF is produced by PSCs and its receptor c-MET is expressed on pancreatic cancer cells and endothelial cells. The current review discusses the role of the MET/HGF axis in tumour progression and dissemination of pancreatic cancer. Therapeutic approaches that were developed targeting either the ligand (HGF) or the receptor (c-MET) have not been shown to translate well into clinical settings. We discuss a two-pronged approach of targeting both the components of this pathway to interrupt the stromal-tumour interactions, which may represent a potential therapeutic strategy to improve outcomes in PC.
Keywords: HGF-c-MET; Pancreatic Cancer; Stromal-tumour interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

