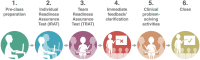
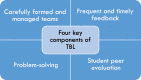
Team-based learning: design, facilitation and participation
- PMID: 33272267
- PMCID: PMC7712595
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-020-02287-y
Team-based learning: design, facilitation and participation
Abstract
Team-based learning (TBL) provides an active, structured form of small group learning, that can be applied to large classes. Student accountability is achieved through the specific steps of TBL, including pre-class preparation, readiness assurance testing, problem-solving activities, and immediate feedback. Globally, a growing number of healthcare faculties have adopted TBL in a variety of combinations, across diverse settings and content areas. This paper provides a succinct overview of TBL and guidance for teachers towards successful design and implementation of TBL within health professional education. It also offers guidance for students participating in TBL. The paper is informed by both educational theory, and the extensive, seven year experience of the first and last authors in designing, implementing, facilitating and evaluating TBL at a large medical school.
Keywords: Clinical problem-solving; Medicine and health curriculum; Problem based learning; Team-based learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Parmelee D, Michaelsen LK, Cook S, Hudes PD. Team-based learning: a practical guide: AMEE guide no 65. Med Teach. 2012;34:e275–e287. - PubMed
-
- Michaelsen LK, Sweet M. The essential elements of team-based learning. New Dir Teach Learn. 2008;116:7–27.
-
- Haidet P, Levine RE, Parmelee DX, Crow S, Kennedy F, Kelly PA, Perkowski L, Michaelsen L, Richards BF. Perspective: guidelines for reporting team based learning activities in the medical and health sciences education literature. Acad Med. 2012;87:292–299. - PubMed
-
- Burgess A, Mellis C. Team-based learning in health care education: maintaining key design elements. J Nurs Care. 2015;S1:007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources