Noncanonical transnitrosylation network contributes to synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 33273062
- PMCID: PMC8091809
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaw0843
Noncanonical transnitrosylation network contributes to synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Here we describe mechanistically distinct enzymes (a kinase, a guanosine triphosphatase, and a ubiquitin protein hydrolase) that function in disparate biochemical pathways and can also act in concert to mediate a series of redox reactions. Each enzyme manifests a second, noncanonical function-transnitrosylation-that triggers a pathological biochemical cascade in mouse models and in humans with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The resulting series of transnitrosylation reactions contributes to synapse loss, the major pathological correlate to cognitive decline in AD. We conclude that enzymes with distinct primary reaction mechanisms can form a completely separate network for aberrant transnitrosylation. This network operates in the postreproductive period, so natural selection against such abnormal activity may be decreased.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
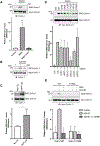

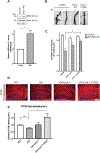
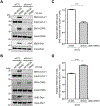
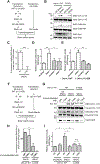
References
-
- Hara MR et al., S-Nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell death by nuclear translocation following Siah1 binding. Nat. Cell Biol 7, 665–674 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Lipton SA et al., A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 364, 626–632 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Hess DT, Matsumoto A, Kim SO, Marshall HE, Stamler JS, Protein S-nitrosylation: purview and parameters. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 6, 150–166 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41 GM103533/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061845/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG065372/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS076411/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003040/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 AG056259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS086890/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA041722/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES016738/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA048882/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

