Evaluation of treatment plan by three-period pulses of high-dose dexamethasone among patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia on platelet count response and adverse events: A randomized Clinical trial
- PMID: 33273933
- PMCID: PMC7698390
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_257_19
Evaluation of treatment plan by three-period pulses of high-dose dexamethasone among patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia on platelet count response and adverse events: A randomized Clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) decreases platelet count as well as increases the risk of bleeding due to platelet destruction in an autoimmune disorder. For many years, prednisone (PDN) has been the standard first-line treatment in ITP practical guidelines. The current randomized clinical trial compared the efficacy of treatments between three-pulse high-dose dexamethasone (HD-DXM) and the traditional PDN regimen among untreated patients with ITP in accordance with platelet count responses and adverse events.
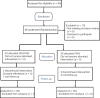
Materials and methods: We randomly assigned eligible patients with ITP to receive PDN or a three-pulse regimen of HD-DXM. In the HD-DXM group, 40 mg of DXM was administered intravenously for 4 consecutive days and was repeated in 14-day intervals for three pulses of treatment. Patients in the PDN group received 1.0 mg/kg of PDN orally per day for 4 consecutive weeks. The Mann-Whitney test was used for comparing the median of platelet count between the two groups, and logistic regression was used to evaluate odds ratio (OR) in the response rate of platelet count between the two groups. Blindness was not applied for both patients and physicians.
Results: The initial response rate of platelet count in the HD-DXM group was significantly higher than the PDN group (P < 0.05). According to the results of logistic regression, the initial and sustained response (SR) rate of platelet count in the HD-DXM group was significantly higher than the PDN group (OR: 5.68 and 4.17, respectively, P < 0.05). In fact, in the HD-DXM group, more patients reached SR after the 8-month follow-up (88.9% vs. 66.6%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In patients with ITP disease who have not received any kind of treatment, HD-DXM was more effective than conventional PDN therapy.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; dexamethasone; immune thrombocytopenia.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- McKenzie CG, Guo L, Freedman J, Semple JW. Cellular immune dysfunction in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) Br J Haematol. 2013;163:10–23. - PubMed
-
- Cuker A, Prak ET, Cines DB. Can immune thrombocytopenia be cured with medical therapy? Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015;41:395–404. - PubMed
-
- Neunert C, Lim W, Crowther M, Cohen A, Solberg L, Jr, Crowther MA, et al. The American Society of Hematology 2011 evidence-based practice guideline for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2011;117:4190–207. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials