Deciphering the modifiers for phenotypic variability of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 33274015
- PMCID: PMC7672940
- DOI: 10.4331/wjbc.v11.i3.99
Deciphering the modifiers for phenotypic variability of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
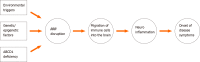
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD), an inborn error of peroxisomal β-oxidation, is caused by defects in the ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily D Member 1 (ABCD1) gene. X-ALD patients may be asymptomatic or present with several clinical phenotypes varying from severe to mild, severe cerebral adrenoleuko-dystrophy to mild adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN). Although most female heterozygotes present with AMN-like symptoms after 60 years of age, occasional cases of females with the cerebral form have been reported. Phenotypic variability has been described within the same kindreds and even among monozygotic twins. There is no association between the nature of ABCD1 mutation and the clinical phenotypes, and the molecular basis of phenotypic variability in X-ALD is yet to be resolved. Various genetic, epigenetic, and environmental influences are speculated to modify the disease onset and severity. In this review, we summarize the observations made in various studies investigating the potential modifying factors regulating the clinical manifestation of X-ALD, which could help understand the pathogenesis of the disease and develop suitable therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Adrenomyelo-neuropathy; Cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy; Modifiers; Phenotypic variation; X-adrenoleukodystrophy.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Moser HW, Mahmood A, Raymond GV. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007;3:140–151. - PubMed
-
- Kemp S, Pujol A, Waterham HR, van Geel BM, Boehm CD, Raymond GV, Cutting GR, Wanders RJ, Moser HW. ABCD1 mutations and the X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutation database: role in diagnosis and clinical correlations. Hum Mutat. 2001;18:499–515. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

