The Relation Between Otolaryngology-Specific Symptoms and Computed Tomography Findings in Ambulatory Care COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 33275032
- PMCID: PMC7720029
- DOI: 10.1177/0145561320975508
The Relation Between Otolaryngology-Specific Symptoms and Computed Tomography Findings in Ambulatory Care COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
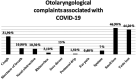
Objective: This study aimed to conduct a study to evaluate the relation between otolaryngology-specific symptoms and computed tomography findings in ambulatory care COVID-19 patients.
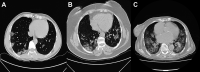
Patient and methods: The study was conducted with medical records of 987 (82%) patients with confirmed COVID-19 virus via real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction between March 11, 2020, and April 21, 2020. Patients were divided into 2 groups as computed tomography (CT)-negative and CT-positive groups considering the presence of the CT findings depicting COVID-19 disease.
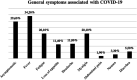
Results: The mean age was significantly higher in CT-positive group than CT-negative group (41.53 ± 12.82 vs 36.61 ± 11.81, P < .001). Cough and shortness of the breath were observed with a significantly higher rate in CT-positive group than that of CT-negative group (44% vs 29.9%, P = .001 and 18.4% vs 9.7%, P = .002, respectively).
Conclusions: In conclusion, advanced age, cough, and shortness of breath could be related to CT scan positivity.
Keywords: anosmia; computed tomography; coronavirus; pandemics; smell disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

