Potential impact of midwives in preventing and reducing maternal and neonatal mortality and stillbirths: a Lives Saved Tool modelling study
- PMID: 33275948
- PMCID: PMC7758876
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30397-1
Potential impact of midwives in preventing and reducing maternal and neonatal mortality and stillbirths: a Lives Saved Tool modelling study
Abstract
Background: Strengthening the capacity of midwives to deliver high-quality maternal and newborn health services has been highlighted as a priority by global health organisations. To support low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) in their decisions about investments in health, we aimed to estimate the potential impact of midwives on reducing maternal and neonatal deaths and stillbirths under several intervention coverage scenarios.
Methods: For this modelling study, we used the Lives Saved Tool to estimate the number of deaths that would be averted by 2035, if coverage of health interventions that can be delivered by professional midwives were scaled up in 88 countries that account for the vast majority of the world's maternal and neonatal deaths and stillbirths. We used four scenarios to assess the effects of increasing the coverage of midwife-delivered interventions by a modest amount (10% every 5 years), a substantial amount (25% every 5 years), and the amount needed to reach universal coverage of these interventions (ie, to 95%); and the effects of coverage attrition (a 2% decrease every 5 years). We grouped countries in three equal-sized groups according to their Human Development Index. Group A included the 30 countries with the lowest HDI, group B included 29 low-to-medium HDI countries, and group C included 29 medium-to-high HDI countries.
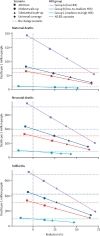
Findings: We estimated that, relative to current coverage, a substantial increase in coverage of midwife-delivered interventions could avert 41% of maternal deaths, 39% of neonatal deaths, and 26% of stillbirths, equating to 2·2 million deaths averted per year by 2035. Even a modest increase in coverage of midwife-delivered interventions could avert 22% of maternal deaths, 23% of neonatal deaths, and 14% of stillbirths, equating to 1·3 million deaths averted per year by 2035. Relative to current coverage, universal coverage of midwife-delivered interventions would avert 67% of maternal deaths, 64% of neonatal deaths, and 65% of stillbirths, allowing 4·3 million lives to be saved annually by 2035. These deaths averted would be particularly concentrated in the group B countries, which currently account for a large proportion of the world's population and have high mortality rates compared with group C.
Interpretation: Midwives can help to substantially reduce maternal and neonatal mortality and stillbirths in LMICs. However, to realise this potential, midwives need to have skills and competencies in line with recommendations from the International Confederation of Midwives, to be part of a team of sufficient size and skill, and to work in an enabling environment. Our study highlights the potential of midwives but there are many challenges to the achievement of this potential. If increased coverage of midwife-delivered interventions can be achieved, health systems will be better able to provide effective coverage of essential sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn, and adolescent health interventions.
Funding: New Venture Fund.
© 2021 This is an Open Access article published under the CC BY 3.0 IGO license which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. In any use of this article, there should be no suggestion that WHO endorses any specific organisation, products or services. The use of the WHO logo is not permitted. This notice should be preserved along with the article's original URL.
Figures

Comment in
-
Scaling up care by midwives must now be a global priority.Lancet Glob Health. 2021 Jan;9(1):e2-e3. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30478-2. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Lancet Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33275951 No abstract available.
References
-
- Every Woman Every Child . Every Woman Every Child; New York: 2015. The global strategy for women's, children's and adolescents' health (2016–2030)
-
- Homer CSE, Friberg IK, Dias MAB. The projected effect of scaling up midwifery. Lancet. 2014;384:1146–1157. - PubMed
-
- Renfrew MJ, McFadden A, Bastos MH. Midwifery and quality care: findings from a new evidence-informed framework for maternal and newborn care. Lancet. 2014;384:1129–1145. - PubMed
-
- UN Population Fund. WHO. International Confederation of Midwives . UN Population Fund; New York: 2014. The state of the world's midwifery 2014: a universal pathway. A woman's right to health.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

