p38γ Activation and BGP (Biliary Glycoprotein) Induction in Primates at Risk for Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer-A Comparative Study with Humans
- PMID: 33276422
- PMCID: PMC7712431
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8040720
p38γ Activation and BGP (Biliary Glycoprotein) Induction in Primates at Risk for Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer-A Comparative Study with Humans
Abstract
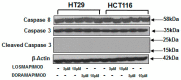
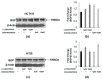
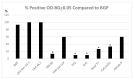
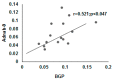
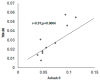
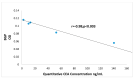
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common cause of cancer-related deaths largely due to CRC liver metastasis (CRLM). Identification of targetable mechanisms continues and includes investigations into the role of inflammatory pathways. Of interest, MAPK is aberrantly expressed in CRC patients, yet the activation status is not defined. The present study assessed p38γ activation in CRC patients, cancer cells, and tissues of cotton top tamarin (CTT) and common marmoset (CM). The primate world is an overlooked resource as colitis-CRC-prone CTT are usually inure to liver metastasis while CM develop colitis but not CRC. The results demonstrate that p38γ protein and phosphorylation levels are significantly increased in CRC patients compared to normal subjects and CTT. Furthermore, p38γ phosphorylation is significantly elevated in human CRC cells and hepatoblastoma cells but not in CM colon. Additionally, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and biliary glycoprotein (BGP) are induced in the CRC patients that showed p38γ phosphorylation. Inhibition of p38 MAPK in CRC cells showed a significant decline in cell growth with no effect on apoptosis or BGP level. Overall, p38γ is activated in CRC tumorigenesis and likely involves CEA antigens during CRLM in humans but not in the CTT or CM, that rarely develop CRLM.
Keywords: BGP; CEA; CRC; blood group antibodies; p38γ; p87; pp38γ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
New World Primates and Their Human Counterparts Share Diseases That Abound with CEACAM and Other Effector Molecules.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 17;15(3):481. doi: 10.3390/life15030481. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40141825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting p38γ to inhibit human colorectal cancer cell progression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Sep 10;517(1):172-179. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.038. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31349971
-
Utility and specificity of plasma heat shock protein 90 alpha, CEA, and CA199 as the diagnostic test in colorectal cancer liver metastasis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Oct;13(5):2497-2504. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-797. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36388698 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of carcinoembryonic antigen and biliary glycoprotein by gamma-interferon.Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1612-9. Cancer Res. 1993. PMID: 8453631
-
Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) and Hepatic Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer: Update on Biomarker for Clinical and Biotechnological Approaches.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2018;12(4):269-279. doi: 10.2174/1872208312666180731104244. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30062978 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting Regression of Barrett's Esophagus-Can All the King's Men Put It Together Again?Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 20;14(9):1182. doi: 10.3390/biom14091182. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334948 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Signatures in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) and Myalgia/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS): Insights from the Fecal Microbiome and Serum Cytokine Profiles.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 25;15(7):928. doi: 10.3390/biom15070928. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723800 Free PMC article.
-
Start Early and See Inflammatory; Late, Nothing Save RAVE: How to Appreciate Radiation Proctitis as a Continuum.Gastro Hep Adv. 2022 Nov 9;2(3):362-369. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2022.11.001. eCollection 2023. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022. PMID: 39132647 Free PMC article.
-
New World Primates and Their Human Counterparts Share Diseases That Abound with CEACAM and Other Effector Molecules.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 17;15(3):481. doi: 10.3390/life15030481. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40141825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of cell-free network communication in alcohol-associated disorders and liver metastasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Nov 7;27(41):7080-7099. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7080. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34887629 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

