microRNA-199a-5p regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic cataract by targeting SP1 gene
- PMID: 33276722
- PMCID: PMC7718685
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-020-00250-7
microRNA-199a-5p regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic cataract by targeting SP1 gene
Abstract
Background: As a common ocular complication of diabetes mellitus, diabetic cataract is becoming a leading cause of visual impairment. The progression of diabetic cataract progression involves epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), the precise role of which remains to be investigated. As microRNAs (miRNAs) are suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of many diseases, identification of aberrantly expressed miRNAs in diabetic lens epithelial cells (LECs) and their targets may provide insights into our understanding of diabetic cataract and potential therapeutic targets.
Methods: Diabetic cataract capsules and LECs exposed to high glucose (25 mmol/L, 1-5 days) were used to mimic the model. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to evaluate the differential expression of miRNA. Dual luciferase reporter assay was used to identify the binding target of miR-199a-5p. The expression of EMT-associated proteins was determined by immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis.
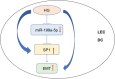
Results: Our results showed the differential expression of miR-9, -16, -22, -199a and -204. MiR-199a was downregulated in diabetic cataract capsule and hyperglycemia-conditioned human LECs. Specific protein 1 could be directly targeted and regulated by miR-199a in LECs and inhibit EMT in diabetic LECs.
Conclusion: Our findings implied miR-199a could be a therapeutic target by regulating SP1 directly to affect EMT in diabetic cataract and provided novel insights into the pathogenesis of diabetic cataract.
Keywords: Diabetic cataract; Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; MiR-199a-5p; Specific protein 1.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Cantini L, Bertoli G, Cava C, Dubois T, Zinovyev A, Caselle M, Castiglioni I, Barillot E, Martignetti L. Identification of microRNA clusters cooperatively acting on epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:2205–2215. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

