Telomere lengths in women treated for breast cancer show associations with chemotherapy, pain symptoms, and cognitive domain measures: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 33276807
- PMCID: PMC7716505
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-020-01368-6
Telomere lengths in women treated for breast cancer show associations with chemotherapy, pain symptoms, and cognitive domain measures: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Survival rates for breast cancer (BC) have improved, but quality of life post-diagnosis/treatment can be adversely affected, with survivors reporting a constellation of psychoneurological symptoms (PNS) including stress, anxiety, depression, pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, and cognitive dysfunction.
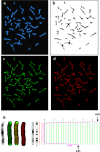
Methods: To assess a potential relationship between telomere length (TL) and the development/persistence of PNS, we longitudinally studied 70 women (ages 23-71) with early stage BC (I-IIIA) at 5 time-points: prior to treatment (baseline), the mid-point of their chemotherapy cycle, 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years following the initiation of chemotherapy. Measures quantified included assessments of each of the PNS noted above and TL [using both a multiplex qPCR assay and a chromosome-specific fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay].
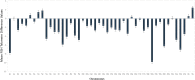
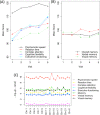
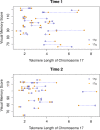
Results: Variables associated with qPCR mean TLs were age (p = 0.004) and race (T/S ratios higher in Blacks than Whites; p = 0.019). Significant differences (mostly decreases) in chromosome-specific TLs were identified for 32 of the 46 chromosomal arms at the mid-chemo time-point (p = 0.004 to 0.049). Unexpectedly, the sequential administration of doxorubicin [Adriamycin], cyclophosphamide [Cytoxan], and docetaxel [Taxotere] (TAC regimen) was consistently associated with higher TLs, when compared to TLs in women receiving a docetaxel [Taxotere], Carboplatin [Paraplatin], and trastuzumab [Herceptin] [TCH] chemotherapy regimen [association was shown with both the qPCR and FISH assays (p = 0.036)]. Of the PNS, pain was significantly negatively associated with TL (higher pain; shorter telomeres) for a subset of chromosomal arms (5q, 8p, 13p, 20p, 22p, Xp, Xq) (p = 0.014-0.047). Chromosomal TLs were also associated with 7 of the 8 cognitive domains evaluated, with the strongest relationship being noted for chromosome 17 and the visual memory domain (shorter telomeres; lower scores).
Conclusions: We showed that race and age were significantly associated with telomere length in women treated for early stage BC and that acquired telomere alterations differed based on the woman's treatment regimen. Our study also demonstrated that pain and cognitive domain measures were significantly related to telomere values in this study cohort. Expanding upon the knowledge gained from this longitudinal study could provide insight about the biological cascade of events that contribute to PNS related to BC and/or its treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Chemotherapy-related cognitive dysfunction; Chromosome-specific telomere lengths; Psychoneurologic symptoms; Telomere.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Perceived Stress Levels, Chemotherapy, Radiation Treatment and Tumor Characteristics Are Associated with a Persistent Increased Frequency of Somatic Chromosomal Instability in Women Diagnosed with Breast Cancer: A One Year Longitudinal Study.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0133380. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133380. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26177092 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive performance in survivors of breast cancer and markers of biological aging.Cancer. 2019 Jan 15;125(2):298-306. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31777. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30474160 Free PMC article.
-
Neural correlates in functional brain mapping among breast cancer survivors receiving different chemotherapy regimens: a qEEG/HEG-based investigation.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov 3;52(11):1253-1264. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyac121. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35946328
-
Telomeric impact of conventional chemotherapy.Front Med. 2013 Dec;7(4):411-7. doi: 10.1007/s11684-013-0293-z. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Front Med. 2013. PMID: 24155095 Review.
-
The relationship between physical activity and telomere length in women: A systematic review.Mech Ageing Dev. 2025 Apr;224:112042. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2025.112042. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Mech Ageing Dev. 2025. PMID: 39983997
Cited by
-
The Cancer Genomic Integration Model for Symptom Science (CGIMSS): A Biopsychosocial Framework.Biol Res Nurs. 2023 Apr;25(2):210-219. doi: 10.1177/10998004221132250. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Biol Res Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36206160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere Length Associates With Symptom Severity After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Older Adults.Neurotrauma Rep. 2023 May 23;4(1):350-358. doi: 10.1089/neur.2023.0012. eCollection 2023. Neurotrauma Rep. 2023. PMID: 37284700 Free PMC article.
-
Chemobrain: An accelerated aging process linking adenosine A2A receptor signaling in cancer survivors.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023;170:267-305. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2023.08.003. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37741694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive adverse effects of chemotherapy and immunotherapy: are interventions within reach?Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Mar;18(3):173-185. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00617-2. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35140379 Review.
-
Cognitive impairments associated with chemotherapy in women with breast cancer: a meta-analysis and meta-regression.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 Oct 13;56:e12947. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e12947. eCollection 2023. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 37851791 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

