Tumor-Infiltrating Natural Killer Cells
- PMID: 33277307
- PMCID: PMC7611243
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0655
Tumor-Infiltrating Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
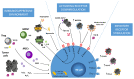
Because of their potent antitumor activity and their proinflammatory role, natural killer (NK) cells are at the forefront of efforts to develop immuno-oncologic treatments. NK cells participate in immune responses to tumors by killing target cells and producing cytokines. However, in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, NK cells become dysfunctional through exposure to inhibitory molecules produced by cancer cells, leading to tumor escape. We provide an overview of what is known about NK tumor infiltration and surveillance and about the mechanisms by which NK cells become dysfunctional. SIGNIFICANCE: The functions of tumor-infiltrating NK cells may be impaired. This review aims to describe the various mechanisms by which tumors alter NK-cell functions.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
B.C, S.C., L.C. and E.V. are employees of Innate Pharma.
Figures

References
-
- Greenberg AH, Hudson L, Shen L, Roitt IM. Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity due to a “Null” Lymphoid Cell. Nat New Biol. 1973;242:111–3. - PubMed
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975;5:112–7. - PubMed
-
- Della Chiesa M, Marcenaro E, Sivori S, Carlomagno S, Pesce S, Moretta A. Human NK cell response to pathogens. Semin Immunol. 2014;26:152–60. - PubMed
-
- Montaldo E, Del Zotto G, Della Chiesa M, Mingari MC, Moretta A, De Maria A, et al. Human NK cell receptors/markers: a tool to analyze NK cell development, subsets and function. Cytometry A. 2013;83A:702–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

