Vaccine-Induced Intratumoral Lymphoid Aggregates Correlate with Survival Following Treatment with a Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Vaccine in Patients with Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33277370
- PMCID: PMC7925374
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2974
Vaccine-Induced Intratumoral Lymphoid Aggregates Correlate with Survival Following Treatment with a Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Vaccine in Patients with Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Immunotherapy is currently ineffective for nearly all pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAC), largely due to its tumor microenvironment (TME) that lacks antigen-experienced T effector cells (Teff). Vaccine-based immunotherapies are known to activate antigen-specific Teffs in the peripheral blood. To evaluate the effect of vaccine therapy on the PDAC TME, we designed a neoadjuvant and adjuvant clinical trial of an irradiated, GM-CSF-secreting, allogeneic PDAC vaccine (GVAX).
Patients and methods: Eighty-seven eligible patients with resectable PDAC were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to receive GVAX alone or in combination with two forms of low-dose cyclophosphamide. Resected tumors following neoadjuvant immunotherapy were assessed for the formation of tertiary lymphoid aggregates (TLA) in response to treatment. The clinical endpoints are disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results: The neoadjuvant treatment with GVAX either alone or with two forms of low-dose cyclophosphamide is safe and feasible without adversely increasing the surgical complication rate. Patients in Arm A who received neoadjuvant and adjuvant GVAX alone had a trend toward longer median OS (35.0 months) than that (24.8 months) in the historical controls who received adjuvant GVAX alone. However, Arm C, who received low-dose oral cyclophosphamide in addition to GVAX, had a significantly shorter DFS than Arm A. When comparing patients with OS > 24 months to those with OS < 15 months, longer OS was found to be associated with higher density of intratumoral TLA.
Conclusions: It is safe and feasible to use a neoadjuvant immunotherapy approach for PDACs to evaluate early biologic responses. In-depth analysis of TLAs is warranted in future neoadjuvant immunotherapy clinical trials.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

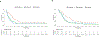
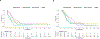
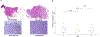
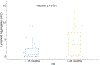
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, et al. Global cancer Observatory: cancer today. Lyon, France: international agency for research on cancer. Cancer Today 2018.
-
- Osipov A, Zaidi N, Laheru DA. Dual Checkpoint Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer: Revealing the Limitations of Synergy and the Potential of Novel Combinations. JAMA oncology 2019;5(10):1438–9. - PubMed
-
- Laheru D, Jaffee EM. Immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer—science driving clinical progress. Nature Reviews Cancer 2005;5(6):459–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

