Small molecule inhibition of Dynamin-dependent endocytosis targets multiple niche signals and impairs leukemia stem cells
- PMID: 33277497
- PMCID: PMC7719179
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20091-6
Small molecule inhibition of Dynamin-dependent endocytosis targets multiple niche signals and impairs leukemia stem cells
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Small molecule inhibition of Dynamin-dependent endocytosis targets multiple niche signals and impairs leukemia stem cells.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 19;12(1):1288. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21688-1. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33608527 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
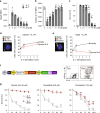
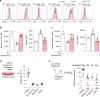
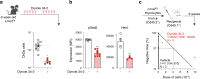
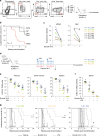
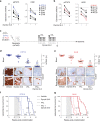
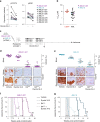
Intensive chemotherapy for acute leukemia can usually induce complete remission, but fails in many patients to eradicate the leukemia stem cells responsible for relapse. There is accumulating evidence that these relapse-inducing cells are maintained and protected by signals provided by the microenvironment. Thus, inhibition of niche signals is a proposed strategy to target leukemia stem cells but this requires knowledge of the critical signals and may be subject to compensatory mechanisms. Signals from the niche require receptor-mediated endocytosis, a generic process dependent on the Dynamin family of large GTPases. Here, we show that Dynole 34-2, a potent inhibitor of Dynamin GTPase activity, can block transduction of key signalling pathways and overcome chemoresistance of leukemia stem cells. Our results provide a significant conceptual advance in therapeutic strategies for acute leukemia that may be applicable to other malignancies in which signals from the niche are involved in disease progression and chemoresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting RSPO3-LGR4 Signaling for Leukemia Stem Cell Eradication in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2020 Aug 10;38(2):263-278.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.05.014. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32559496
-
In vivo targeting of leukemia stem cells by directing parthenolide-loaded nanoparticles to the bone marrow niche.Leukemia. 2016 Jul;30(7):1582-6. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.343. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Leukemia. 2016. PMID: 26669973 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Myeloid malignancies and the microenvironment.Blood. 2017 Feb 16;129(7):811-822. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-670224. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28064238 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the bone marrow microenvironment in acute leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Nov;59(11):2535-2545. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1434886. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 29431560 Review.
-
Targeting membrane trafficking in infection prophylaxis: dynamin inhibitors.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;23(2):90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Nov 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23164733 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamin Inhibitors Prevent the Establishment of the Cytomegalovirus Assembly Compartment in the Early Phase of Infection.Life (Basel). 2021 Aug 25;11(9):876. doi: 10.3390/life11090876. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575026 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer ATF4-mediated CD58 endocytosis impairs anti-tumor immunity and immunotherapy.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 25;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06245-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40001116 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytosis in cancer and cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2023 Jul;23(7):450-473. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00574-6. Epub 2023 May 22. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37217781 Review.
-
Dynamin inhibition causes context-dependent cell death of leukemia and lymphoma cells.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 7;16(9):e0256708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256708. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34492077 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting pyroptosis with nanoparticles to alleviate neuroinflammatory for preventing secondary damage following traumatic brain injury.Sci Adv. 2024 Jan 12;10(2):eadj4260. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj4260. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38198543 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

