Improvement in fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective multicentre study of 36,935 procedures from 2010 to 2017
- PMID: 33277508
- PMCID: PMC7718264
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77127-6
Improvement in fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective multicentre study of 36,935 procedures from 2010 to 2017
Abstract
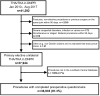
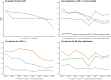
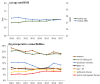
"Fast-track" protocols has improved surgical care with a reduction in length of hospital stay (LOS) in total hip (THA) and knee arthroplasty (TKA). However, the effects of continuous refinement of perioperative care lack detailed assessment. We studied time-related changes in LOS and morbidity after THA and TKA within a collaboration with continuous scientific refinement of perioperative care. Prospective multicentre consecutive cohort study between 2010 and 2017 from nine high-volume orthopaedic centres with established fast-track THA and TKA protocols. Prospective collection of comorbidities and complete 90-day follow-up from the Danish National Patient Registry and medical records. Of 36,935 procedures median age was 69 [62 to 75] years and 58% women. LOS declined from three [two to three] days in 2010 to one [one to two] day in 2017. LOS > 4 days due to "medical" or "surgical" complications, and "with no recorded morbidity" declined from 4.4 to 2.7%, 1.5 to 0.6%, and 3.8 to 1.3%, respectively. 90-days readmission rate declined from 8.6 to 7.7%. Our multicentre study in a socialized healthcare setting was associated with a continuous reduction in LOS and morbidity after THA and TKA.
Conflict of interest statement
PBP received an unconditional PhD grant from The Lundbeck Foundation [R230-2017-166] which took no part in study design, collection, analysis or interpretation of data, writing the report or the decision to submit the report for publication; HK is advisory board member at “Rapid Recovery” by Zimmer Biomet, outside the submitted work; CCJ has nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

