Pseudoginsenoside-F11 attenuates cognitive dysfunction and tau phosphorylation in sporadic Alzheimer's disease rat model
- PMID: 33277592
- PMCID: PMC8379201
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-020-00562-8
Pseudoginsenoside-F11 attenuates cognitive dysfunction and tau phosphorylation in sporadic Alzheimer's disease rat model
Abstract
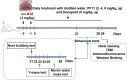
We previously reported that pseudoginsenoside-F11 (PF11), an ocotillol-type saponin, significantly ameliorated Alzheimer's disease (AD)-associated cognitive defects in APP/PS1 and SAMP8 mice by inhibiting Aβ aggregation and tau hyperphosphorylation, suggesting a potential therapeutic effect of PF11 in the treatment of AD. In the present study we further evaluated the therapeutic effects of PF11 on relieving cognitive impairment in a rat model of sporadic AD (SAD). SAD was induced in rats by bilateral icv infusion of streptozotocin (STZ, 3 mg/kg). The rats were treated with PF11 (2, 4, 8 mg·kg-1·d-1, ig) or a positive control drug donepezil (5 mg·kg-1·d-1, ig) for 4 weeks. Their cognitive function was assessed in the nest building, Y-maze, and Morris water maze tests. We showed that STZ icv infusion significantly affected the cognitive function, tau phosphorylation, and insulin signaling pathway in the hippocampus. Furthermore, STZ icv infusion resulted in significant upregulation of the calpain I/cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDK5) signaling pathway in the hippocampus. Oral administration of PF11 dose-dependently ameliorated STZ-induced learning and memory defects. In addition, PF11 treatment markedly reduced the neuronal loss, protected the synapse structure, and modulated STZ-induced expression of tau phosphorylation by regulating the insulin signaling pathway and calpain I/CDK5 signaling pathway in the hippocampus. Donepezil treatment exerted similar beneficial effects in STZ-infused rats as the high dose of PF11 did. This study highlights the excellent therapeutic potential of PF11 in managing AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Tau hyperphosphorylation; calpain I/CDK5 signaling pathway; donepezil; insulin signaling pathway; pseudoginsenoside-F11.
© 2020. CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Rasheed NOA. Study of the possible protective effect of formoterol in streptozotocin-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Doctor of Philosophy degree. Cairo: Cairo University; 2019.
-
- Ponce-Lopez T, Hong E, Abascal-Díaz M, Meneses A. Role of GSK3β and PP2A on regulation of tau phosphorylation in hippocampus and memory impairment in ICV-STZ animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Alzheimer Dis. 2017;06:13–31. doi: 10.4236/aad.2017.61002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

