Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery
- PMID: 33277608
- PMCID: PMC7717100
- DOI: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery
Abstract
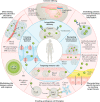
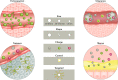
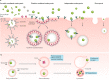
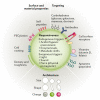
In recent years, the development of nanoparticles has expanded into a broad range of clinical applications. Nanoparticles have been developed to overcome the limitations of free therapeutics and navigate biological barriers - systemic, microenvironmental and cellular - that are heterogeneous across patient populations and diseases. Overcoming this patient heterogeneity has also been accomplished through precision therapeutics, in which personalized interventions have enhanced therapeutic efficacy. However, nanoparticle development continues to focus on optimizing delivery platforms with a one-size-fits-all solution. As lipid-based, polymeric and inorganic nanoparticles are engineered in increasingly specified ways, they can begin to be optimized for drug delivery in a more personalized manner, entering the era of precision medicine. In this Review, we discuss advanced nanoparticle designs utilized in both non-personalized and precision applications that could be applied to improve precision therapies. We focus on advances in nanoparticle design that overcome heterogeneous barriers to delivery, arguing that intelligent nanoparticle design can improve efficacy in general delivery applications while enabling tailored designs for precision applications, thereby ultimately improving patient outcome overall.
Conflict of interest statement
A list of entities with which R.L. is involved, compensated or uncompensated, can be found in the Supplementary information. M.J.M., M.M.B., R.M.H., M.E.W. and N.A.P. declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- The White House Office of the Press Secretary. National Nanotechnology Initiative: leading to the next industrial revolution. White Househttps://clintonwhitehouse4.archives.gov/WH/New/html/20000121_4.html (2000).
-
- Mitragotri S, et al. Drug delivery research for the future: expanding the nano horizons and beyond. J. Control. Release. 2017;246:183–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

