[Toxic shock syndrome due to Staphylococcus aureus in a small child, a (clinical or laboratory chemical) visual diagnosis?]
- PMID: 33281225
- PMCID: PMC7702684
- DOI: 10.1007/s00112-020-01075-8
[Toxic shock syndrome due to Staphylococcus aureus in a small child, a (clinical or laboratory chemical) visual diagnosis?]
Abstract
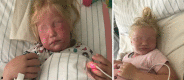
It is reported about the case of a 3-year-old girl who was admitted to hospital with high fever, vomiting, skin rash, dehydration, suspected staphyloderma and for exclusion of a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2-infection (SARS-CoV‑2 infection). The suspicion of a toxic shock syndrome, among other inflammatory diseases as differential diagnoses, was based on profound erythroderma and arterial hypotension. The diagnostic pathway, treatment and clinical course of this rare disease are described.
Vorgestellt wird der Fall eines 3‑jährigen Mädchens, das mit hohem Fieber, Erbrechen, unklarem Exanthem, Dehydratation, Verdacht auf Staphylodermie und zum Ausschluss einer SARS-CoV-2-Infektion (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2) stationär eingewiesen wurde. Der Verdacht auf ein toxisches Schocksyndrom kam durch eine erhebliche Erythrodermie und arterielle Hypotonie auf; andere Inflammationskrankheiten standen zur Differenzialdiagnostik. Der diagnostische Pfad, die Therapie und der klinische Verlauf dieser seltenen Erkrankung werden beschrieben.
Keywords: Pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome; Staphylococci; TSST‑1; Toxin producer; Toxin-mediated infection.
© Springer Medizin Verlag GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature 2020.
References
-
- Becker K, Roth R, Peters G. Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36(9):2548–2553. doi: 10.1128/JCM.36.9.2548-2553.1998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Reduced incidence of menstrual toxic-shock syndrome—United States 1980–1990. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1990;39:421. - PubMed
-
- Delisle B. Das Toxische- Schocksyndrom aus kinder- und Jugendgynäkologischer Sicht. Korasion. 2019;04:33–37.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous