Phosphorylation Modifications Regulating Cardiac Protein Quality Control Mechanisms
- PMID: 33281625
- PMCID: PMC7689282
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.593585
Phosphorylation Modifications Regulating Cardiac Protein Quality Control Mechanisms
Abstract
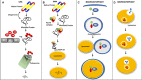
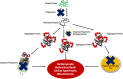
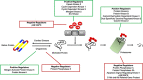
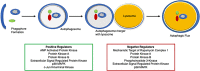
Many forms of cardiac disease, including heart failure, present with inadequate protein quality control (PQC). Pathological conditions often involve impaired removal of terminally misfolded proteins. This results in the formation of large protein aggregates, which further reduce cellular viability and cardiac function. Cardiomyocytes have an intricately collaborative PQC system to minimize cellular proteotoxicity. Increased expression of chaperones or enhanced clearance of misfolded proteins either by the proteasome or lysosome has been demonstrated to attenuate disease pathogenesis, whereas reduced PQC exacerbates pathogenesis. Recent studies have revealed that phosphorylation of key proteins has a potent regulatory role, both promoting and hindering the PQC machinery. This review highlights the recent advances in phosphorylations regulating PQC, the impact in cardiac pathology, and the therapeutic opportunities presented by harnessing these modifications.
Keywords: autophagy; cardiac disease; chaperones; phosphorylation; proteasome; ubiquitin enzymes.
Copyright © 2020 Mishra, Dunkerly-Eyring, Keceli and Ranek.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein Quality Control by Molecular Chaperones in Neurodegeneration.Front Neurosci. 2017 Apr 6;11:185. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00185. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28428740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Protein Quality Control in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: From Bench to Bedside.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Oct 15;7:585309. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.585309. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 33195472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated protein quality control in cardiomyocytes.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jan 1;21(1):192-202. doi: 10.2741/4384. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 26709769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Protein Kinase G to Treat Cardiac Proteotoxicity.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 28;11:858. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00858. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32848832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posttranslational modification and quality control.Circ Res. 2013 Jan 18;112(2):367-81. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.268706. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23329792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heat Shock Protein 90 as Therapeutic Target for CVDs and Heart Ageing.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 7;23(2):649. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020649. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal dependent protein phosphatase PPM family in cardiac health and diseases.Cell Signal. 2021 Sep;85:110061. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110061. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34091011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mechanosignaling in the control of myocardial mass.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Mar 1;328(3):H622-H638. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00277.2024. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39739566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of HSP90 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases.Cells. 2022 Oct 31;11(21):3444. doi: 10.3390/cells11213444. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does an apple a day keep away diseases? Evidence and mechanism of action.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 20;11(9):4926-4947. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3487. eCollection 2023 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37701204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

