ACE2 partially dictates the host range and tropism of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33282147
- PMCID: PMC7700767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.032
ACE2 partially dictates the host range and tropism of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
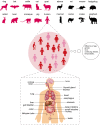
COVID-19, which is caused by SARS-CoV-2, has been declared a global pandemic. Although effective strategies have been applied to treat the disease, much is still unknown about this novel virus. SARS-CoV-2 enters host cells through ACE2, which is a component of the angiotensin-regulating system. Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein to ACE2 is a prerequisite for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Many studies have indicated a close relationship between ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 infection. The structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2 has been analyzed in detail. The diversification of the ACE2 sequence due to ACE2 polymorphisms and alternative splicing has to a large extent affected the susceptibility of different species. Differential ACE2 expression makes specific populations more prone to be infected, and ACE2 also plays a role in the broad tropism of SARS-CoV-2 in human organs and tissues. In this review, we comprehensively summarize how the ACE2 expression profile affects the host range and tropism of SARS-CoV-2, which will provide mechanistic insights into the susceptibilities and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; Host range; Host tropism; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Lan J., Ge J., Yu J., Shan S., Zhou H., Fan S. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2020;581(7807):221–224. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
