Effect of locally delivered doxycycline as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of periodontitis in smokers: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
- PMID: 33282148
- PMCID: PMC7688043
Effect of locally delivered doxycycline as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of periodontitis in smokers: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Abstract
Background: Scaling and root planing (SRP) for the treatment of periodontitis may be less effective in some patients. This study evaluated the effectiveness of local doxycycline as an adjunct to SRP among smokers with periodontitis compared to SRP alone in randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Materials and methods: For this systematic review and meta-analysis, PubMed and Scopus databases were searched till November 2018 for English publications. RCTs that compared the effect of local doxycycline adjunct to SRP among smokers with periodontitis were selected. Patient characteristics, disease characteristics, and outcome data on clinical attachment level (CAL) and periodontal probing depth at 1, 3- and 6-month follow-up was extracted. Quality of selected studies was assessed by the revised Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Random effects model and trial sequential analysis were performed. GRADE approach was used to assess the quality of evidence. P > 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
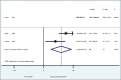
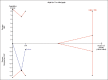
Results: Five trials were included in the review. Local use of doxycycline as an adjunct to SRP was effective in gain of 1.1 mm (0.47-1.74, P = 0.091) in CAL at 6 months calculated from two studies. The evidence was of low quality, and at least a total of 866 patients are required for conclusiveness.
Conclusion: Local doxycycline as an adjunct to SRP significantly improved clinical attachment in smokers with periodontitis and can be recommended. Studies are required with long-term follow-up and patient-related outcome data.
Keywords: Dental scaling; doxycycline; periodontitis; root planing; smokers.
Copyright: © 2020 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or nonfinancial in this article.
Figures
References
-
- van Winkelhoff AJ, Loos BG, van der Reijden WA, van der Velden U. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Bacteroides forsythus and other putative periodontal pathogens in subjects with and without periodontal destruction. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29:1023–8. - PubMed
-
- Doungudomdacha S, Rawlinson A, Walsh TF, Douglas CW. Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on clinical parameters and the numbers of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans at adult periodontitis sites. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28:437–45. - PubMed
-
- Van der Weijden GA, Timmerman MF. A systematic review on the clinical efficacy of subgingival debridement in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29(Suppl 3):55–71. - PubMed
-
- Renvert S, Wikström M, Dahlén G, Slots J, Egelberg J. On the inability of root debridement and periodontal surgery to eliminate Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans from periodontal pockets. J Clin Periodontol. 1990;17:351–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources