Changing paradigm in advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33282404
- PMCID: PMC7711369
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-20-1472
Changing paradigm in advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
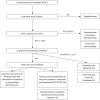
Lung cancer is the most common cancer worldwide. Approximately 18% of all deaths related to cancer are associated with lung cancer. Management of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been changing rapidly in last few years. For patients with unresectable non-metastatic disease, maintenance durvalumab is now given after offering chemo-radiation concurrently based on the result from the PACIFIC trial. Management of metastatic disease greatly depends on the status of sensitizing driver mutation and PD-L1 level of the tumor cells. In this review article, we will summarize the outcome of various clinical trials and will provide the most up-to-date information on the management of patients with advanced and metastatic NSCLC.
Keywords: Advanced; lung cancer; metastatic; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); stage III; stage IV.
2020 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd-20-1472). The series “Contemporary Practice in Thoracic Neoplasm Diagnosis, Evaluation and Treatment” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. Dr. KP reports personal fees from Astra-Zeneca. Dr. KL reports honoraria from Onc Live and Takeda. Dr. AD reports personal fees from Roche/Genentech, personal fees from OncLive. The other authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials