Analysis of attenuation coefficient estimation in Fourier-domain OCT of semi-infinite media
- PMID: 33282477
- PMCID: PMC7687928
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.403283
Analysis of attenuation coefficient estimation in Fourier-domain OCT of semi-infinite media
Abstract
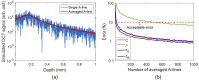
The attenuation coefficient (AC) is an optical property of tissue that can be estimated from optical coherence tomography (OCT) data. In this paper, we aim to estimate the AC accurately by compensating for the shape of the focused beam. For this, we propose a method to estimate the axial PSF model parameters and AC by fitting a model for an OCT signal in a homogenous sample to the recorded OCT signal. In addition, we employ numerical analysis to obtain the theoretical optimal precision of the estimated parameters for different experimental setups. Finally, the method is applied to OCT B-scans obtained from homogeneous samples. The numerical and experimental results show accurate estimations of the AC and the focus location when the focus is located inside the sample.
© 2020 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Barwari K., de Bruin D. M., Faber D. J., van Leeuwen T. G., de la Rosette J. J., Laguna M. P., “Differentiation between normal renal tissue and renal tumors using functional optical coherence tomography: a phase I in vivo human study,” BJU Int. 110(8b), E415–E420 (2012).10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11197.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
