Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) and Atherosclerosis: A Mechanistic and Pharmacological Review
- PMID: 33282862
- PMCID: PMC7688915
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.581015
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) and Atherosclerosis: A Mechanistic and Pharmacological Review
Abstract
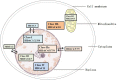
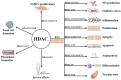
Atherosclerosis (AS), the most common underlying pathology for coronary artery disease, is a chronic inflammatory, proliferative disease in large- and medium-sized arteries. The vascular endothelium is important for maintaining vascular health. Endothelial dysfunction is a critical early event leading to AS, which is a major risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction. Accumulating evidence has suggested the critical roles of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in regulating vascular cell homeostasis and AS. The purpose of this review is to present an updated view on the roles of HDACs (Class I, Class II, Class IV) and HDAC inhibitors in vascular dysfunction and AS. We also elaborate on the novel therapeutic targets and agents in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: HDAC inhibitors; atherosclerosis; endothelial dysfunction; epigenetic; histone deacetylation; macrophage; smooth muscle cells.
Copyright © 2020 Chen, He, Fu, Sahebkar, Tan, Xu and Li.
Figures
References
-
- Ali M. M., Mahmoud A. M., Le Master E., Levitan I., Phillips S. A. (2019). Role of matrix metalloproteinases and histone deacetylase in oxidative stress-induced degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 316 H647–H663. 10.1152/ajpheart.00090.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials