Differentially Expressed mRNAs and Their Long Noncoding RNA Regulatory Network with Helicobacter pylori-Associated Diseases including Atrophic Gastritis and Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 33282942
- PMCID: PMC7686847
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3012193
Differentially Expressed mRNAs and Their Long Noncoding RNA Regulatory Network with Helicobacter pylori-Associated Diseases including Atrophic Gastritis and Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Background: Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection is the strongest risk factor for gastric cancer (GC). However, the mechanisms of Hp-associated GC remain to be explored.
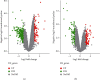
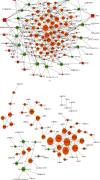
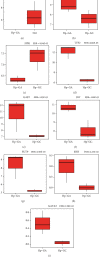
Methods: The gene expression profiling (GSE111762) data were downloaded from the GEO database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between normal samples (NO) and Hp-atrophic gastritis (GA) or Hp-GA and Hp-GC were identified by GEO2R. Gene Ontology and pathway enrichment analysis were performed using the DAVID database. lncRNA-TF-mRNA and ceRNA regulation networks were constructed using Cytoscape. The cross-networks were obtained by overlapping molecules of the above two networks. GSE27411 and GSE116312 datasets were employed for validation.
Results: DEGs between NO and Hp-GA are linked to the activity of inward rectifying potassium channels, digestion, etc. DEGs between Hp-GA and Hp-GC were associated with digestion, positive regulation of cell proliferation, etc. According to the lncRNA-TF-mRNA network, 63 lncRNAs, 12 TFs, and 209 mRNAs were involved in Hp-GA while 16 lncRNAs, 11 TFs, and 92 mRNAs were contained in the Hp-GC network. In terms of the ceRNA network, 120 mRNAs, 18 miRNAs, and 27 lncRNAs were shown in Hp-GA while 72 mRNAs, 8 miRNAs, and 1 lncRNA were included in the Hp-GC network. In the cross-network, we found that immune regulation and differentiation regulation were important in the process of NO-GA. Neuroendocrine regulation was mainly related to the process of GA-GC. In the end, we verified that CDX2 plays an important role in the pathological process of NO to Hp-GA. Comparing Hp-GA with Hp-GC, DEGs (FPR1, TFF2, GAST, SST, FUT9, and SHH), TF, and GATA5 were of great significance.
Conclusions: We identified the DEGs, and their lncRNA regulatory network of Hp-associated diseases might provide insights into the mechanism between Hp infection and GC. Furthermore, in-depth studies of the molecules might be useful to explore the multistep process of gastric diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Songyi Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Holleczek B., Schottker B., Brenner H. Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic atrophic gastritis and risk of stomach and esophagus cancer: results from the prospective population-based ESTHER cohort study. International Journal of Cancer. 2020;146(10):2773–2783. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32610. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

