Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, the complement system, the kallikrein-kinin system, type-2 diabetes, interleukin-6, and their interactions regarding the complex COVID-19 pathophysiological crossroads
- PMID: 33283602
- PMCID: PMC7724427
- DOI: 10.1177/1470320320979097
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, the complement system, the kallikrein-kinin system, type-2 diabetes, interleukin-6, and their interactions regarding the complex COVID-19 pathophysiological crossroads
Abstract
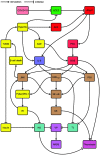
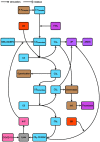
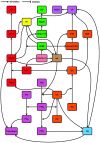
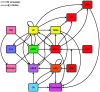
Because of the current COVID-19-pandemic, the world is currently being held hostage in various lockdowns. ACE2 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell-entry, and is at the very center of several pathophysiological pathways regarding the RAAS, CS, KKS, T2DM, and IL-6. Their interactions with severe COVID-19 complications (e.g. ARDS and thrombosis), and potential therapeutic targets for pharmacological intervention, will be reviewed.
Keywords: COVID-19; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; complement; diabetes; interleukin-6; kallikrein-kinin system; renin angiotensin aldosterone system; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone and Kinin-Kallikrein Systems in the Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19 and Long COVID.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 31;22(15):8255. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158255. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What would Sérgio Ferreira say to your physician in this war against COVID-19: How about kallikrein/kinin system?Med Hypotheses. 2020 Oct;143:109886. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109886. Epub 2020 May 30. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32504925 Free PMC article.
-
Aprotinin (I): Understanding the Role of Host Proteases in COVID-19 and the Importance of Pharmacologically Regulating Their Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7553. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147553. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme 2 and Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19: An Update.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021 Mar;28(2):129-139. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00439-9. Epub 2021 Feb 26. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021. PMID: 33635533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and COVID-19: the ominous duet affecting the renin-angiotensin system.Minerva Endocrinol (Torino). 2021 Jun;46(2):193-201. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6507.20.03402-1. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Minerva Endocrinol (Torino). 2021. PMID: 33435650 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of clinical characteristics, antidiabetic and cardiovascular agents with diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: a 7-month follow-up cohort study.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021 Nov 8;20(2):1545-1555. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00901-4. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34778117 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in a Patient with COVID-19 and Associated Sepsis-Induced Neutropenia.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Jan 24;57(2):106. doi: 10.3390/medicina57020106. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33498929 Free PMC article.
-
The home-based breathing and chest mobility exercise improves cardiorespiratory functional capacity in long COVID with cardiovascular comorbidities: a randomized study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Oct 18;24(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04196-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39425012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

