Prothrombin complex concentrate vs. fresh frozen plasma in adult patients undergoing heart surgery - a pilot randomised controlled trial (PROPHESY trial)
- PMID: 33285008
- PMCID: PMC8246985
- DOI: 10.1111/anae.15327
Prothrombin complex concentrate vs. fresh frozen plasma in adult patients undergoing heart surgery - a pilot randomised controlled trial (PROPHESY trial)
Abstract
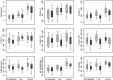
There is equipoise regarding the use of prothrombin complex concentrate vs. fresh frozen plasma in bleeding patients undergoing cardiac surgery. We performed a pilot randomised controlled trial to determine the recruitment rate for a large trial, comparing the impact of prothrombin complex concentrate vs. fresh frozen plasma on haemostasis (1 h and 24 h post-intervention), and assessing safety. Adult patients who developed bleeding within 24 h of cardiac surgery that required coagulation factor replacement were randomly allocated to receive prothrombin complex concentrate (15 IU.kg-1 based on factor IX) or fresh frozen plasma (15 ml.kg-1 ). If bleeding continued after the first administration of prothrombin complex concentrate or fresh frozen plasma administration, standard care was administered. From February 2019 to October 2019, 180 patients were screened, of which 134 (74.4% (95%CI 67-81%)) consented, 59 bled excessively and 50 were randomly allocated; 25 in each arm, recruitment rate 35% (95%CI 27-44%). There were 23 trial protocol deviations, 137 adverse events (75 prothrombin complex concentrate vs. 62 fresh frozen plasma) and 18 serious adverse events (5 prothrombin complex concentrate vs. 13 fresh frozen plasma). There was no increase in thromboembolic events with prothrombin complex concentrate. No patient withdrew from the study, four were lost to follow-up and two died. At 1 h after administration of the intervention there was a significant increase in fibrinogen, Factor V, Factor XII, Factor XIII, α2 -antiplasmin and antithrombin levels in the fresh frozen plasma arm, while Factor II and Factor X were significantly higher in the prothrombin complex concentrate group. At 24 h, there were no significant differences in clotting factor levels. We conclude that recruitment to a larger study is feasible. Haemostatic tests have provided useful insight into the haemostatic changes following prothrombin complex concentrate or fresh frozen plasma administration. A definitive trial is needed to ascertain the benefits and safety for each.
Keywords: FFP; PCC; bleeding; cardiac surgery; randomised trial.
© 2020 The Authors. Anaesthesia published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association of Anaesthetists.
Figures
References
-
- Murphy GJ, Reeves BC, Rogers CA, Rizvi SI, Culliford L, Angelini GD. Increased mortality, postoperative morbidity, and cost after red blood cell transfusion in patients having cardiac surgery. Circulation 2007; 116: 2544–52. - PubMed
-
- Hunt BJ, Allard S, Keeling D, et al. A practical guideline for the haematological management of major haemorrhage. British Journal of Haematologyy 2015; 170: 788–803. - PubMed
-
- Transfusion NCAoB Audit of Blood Transfusion in Adult Cardiac Surgery. 2011. https://nhsbtdbe.blob.core.windows.net/umbraco‐assets‐corp/14923/nca‐201... (accessed 30/10/2020).
-
- Roman M, Biancari F, Ahmed AB, et al. Prothrombin complex concentrate in cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2019; 107: 1275–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

