Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) universal screening in gravids during labor and delivery
- PMID: 33285496
- PMCID: PMC7706716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.11.069
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) universal screening in gravids during labor and delivery
Abstract
Objective: To screen pregnant women at risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection during delivery using reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test and serum immunoglobulin (Ig) testing.
Method: Between March 31 st and August 31 st of 2020, consecutive pregnant women admitted for labor and delivery in a single hospital were screened for SARS-CoV-2 with nasopharyngeal RT-PCR swab tests and detection of serum IgG and IgM.
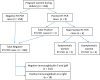
Results: We studied 266 pregnant women admitted for labor and delivery. The prevalence of acute or past SARS-CoV-2 infection was 9.0 %, including (i) two cases with respiratory symptoms of SARS-Co-V-2 infection and positive RT-PCR; (ii) four asymptomatic women with positive RT-PCR without clinical symptoms and negative serological tests between two and 15 weeks later; and (iii) two women with false positive RT-PCR due to technical problems. All newborns of the 6 pregnant women with RT-PCR positive had negative RT-PCR and did not require Neonatal Intensive Care Unit admission. There were eighteen asymptomatic women with positive serological IgG tests and negative RT-PCR.
Conclusion: In our cohort of gravids, we found 2.2 % of women with positive RT-PRC tests and 6.7 % with positive serological tests during the first wave of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Delivery; Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); SARS-CoV-2; Screening; serum immunoglobulins.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors report no conflicts of interest and are alone responsible for the content and the writing of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Screening of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection during labor and delivery using polymerase chain reaction and immunoglobulin testing.Life Sci. 2021 Apr 15;271:119200. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119200. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33577855 Free PMC article.
-
Questionnaire-based vs universal PCR testing for SARS-CoV-2 in women admitted for delivery.Birth. 2021 Mar;48(1):96-103. doi: 10.1111/birt.12520. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Birth. 2021. PMID: 33263210 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between viral load, infection-to-delivery interval and mother-to-child transfer of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Jun;57(6):974-978. doi: 10.1002/uog.23639. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33798280 Free PMC article.
-
Samba II PCR testing for COVID-19 in pregnant women: a retrospective cohort study and literature review.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Mar 17;21(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-03653-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 33731037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Mode of Delivery during COVID-19 between December 2019 and April 2020.Am J Perinatol. 2021 Mar;38(4):332-341. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1721658. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Am J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 33285608
Cited by
-
Effects of COVID-19 on Pregnant Women and Newborns: A Review.Cureus. 2022 Oct 21;14(10):e30555. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30555. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36415402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chest imaging in pregnant patients with COVID-19: Recommendations, justification, and optimization.Acta Radiol Open. 2022 Mar 7;11(2):20584601221077394. doi: 10.1177/20584601221077394. eCollection 2022 Feb. Acta Radiol Open. 2022. PMID: 35284094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Universal Testing Policy for COVID-19 in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 8;10:588269. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.588269. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35211434 Free PMC article.
-
Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 24;118(34):e2109229118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2109229118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34376550 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Maternal and Newborn Disease and Related Control for COVID-19.SN Compr Clin Med. 2021;3(6):1272-1294. doi: 10.1007/s42399-021-00836-0. Epub 2021 Mar 17. SN Compr Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33754135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Savirón-Cornudella R., Altamirano-Barcia I.E., Chedraui P., Andeyro-García M., Tajada M., Pérez-López F.R. The coronavirus disease (COVID) 2019 and human pregnancy: A scoping review. Gynecol Reprod Endocrinol Metab. 2020;1(2):70–75. https://gremjournal.com/journal/02-2020/the-coronavirus-disease-covid-20...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous