Asymmetric Contrarians in Opinion Dynamics
- PMID: 33285800
- PMCID: PMC7516446
- DOI: 10.3390/e22010025
Asymmetric Contrarians in Opinion Dynamics
Abstract
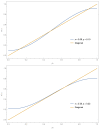
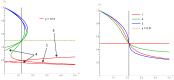
Asymmetry in contrarian behavior is investigated within the Galam model of opinion dynamics using update groups of size 3 with two competing opinions A and B. Denoting x and y the respective proportions of A and B contrarians, four schemes of implementations are studied. The first scheme activates contrarians after each series of updates with probabilities x and y for agents holding respectively opinion A and B. Second scheme activates contrarians within the update groups only against global majority with probability x when A is the majority and y when B is the majority. The third scheme considers in-group contrarians acting prior to the local majority update against both local majority and minority opinions. The last scheme activates in-group contrarians prior to the local majority update but only against the local majority. The main result is the loss of the fifty-fifty attractor produced by symmetric contrarians. Producing a bit less contrarians on its own side than the other side becomes the key to win a public debate, which in turn can guarantee an election victory. The associated phase diagram of opinion dynamics is found to exhibit a rich variety of counterintuitive results.
Keywords: local and global majority; opinion dynamics; sociophysics; tipping points.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Noorazar H., Vixie K.R., Talebanpour A., Hu Y. From classical to modern opinion dynamics. arXiv. 20191909.12089v2
-
- Calvão A.M., Ramos M., Anteneodo C. Role of the plurality rule in multiple choices. J. Stat. Mech. 2016;2016:023405. doi: 10.1088/1742-5468/2016/02/023405. - DOI
-
- Ajmone Marsan G., Bellomo N., Gibelli L. Stochastic evolutionary differential games toward a systems theory of behavioral social dynamics. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 2016;26:1051–1093. doi: 10.1142/S0218202516500251. - DOI
-
- Carbone G., Giannoccaro I. Model of human collective decision-making in complex environments. Eur. Phys. J. 2015;88:339. doi: 10.1140/epjb/e2015-60609-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

