Variational Information Bottleneck for Unsupervised Clustering: Deep Gaussian Mixture Embedding
- PMID: 33285988
- PMCID: PMC7516645
- DOI: 10.3390/e22020213
Variational Information Bottleneck for Unsupervised Clustering: Deep Gaussian Mixture Embedding
Abstract
In this paper, we develop an unsupervised generative clustering framework that combines the variational information bottleneck and the Gaussian mixture model. Specifically, in our approach, we use the variational information bottleneck method and model the latent space as a mixture of Gaussians. We derive a bound on the cost function of our model that generalizes the Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO) and provide a variational inference type algorithm that allows computing it. In the algorithm, the coders' mappings are parametrized using neural networks, and the bound is approximated by Markov sampling and optimized with stochastic gradient descent. Numerical results on real datasets are provided to support the efficiency of our method.
Keywords: Gaussian mixture model; clustering; information bottleneck; unsupervised learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


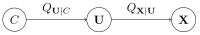


References
-
- Sculley D. Web-scale K-means clustering; Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web; Raleigh, NC, USA. 26–30 April 2010; pp. 1177–1178.
-
- Huang Z. Extensions to the k-means algorithm for clustering large datasets with categorical values. Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 1998;2:283–304. doi: 10.1023/A:1009769707641. - DOI
-
- Hartigan J.A., Wong M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A K-means clustering algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1979;28:100–108. doi: 10.2307/2346830. - DOI
-
- Dempster A.P., Laird N.M., Rubin D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1977;39:1–38.
-
- Ding C., He X. K-means clustering via principal component analysis; Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Machine Learning; Banff, AB, Canada. 4–8 July 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

