An Entropy-Based Approach for Anomaly Detection in Activities of Daily Living in the Presence of a Visitor
- PMID: 33286616
- PMCID: PMC7517444
- DOI: 10.3390/e22080845
An Entropy-Based Approach for Anomaly Detection in Activities of Daily Living in the Presence of a Visitor
Abstract
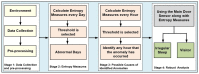
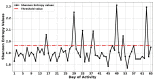
This paper presents anomaly detection in activities of daily living based on entropy measures. It is shown that the proposed approach will identify anomalies when there are visitors representing a multi-occupant environment. Residents often receive visits from family members or health care workers. Therefore, the residents' activity is expected to be different when there is a visitor, which could be considered as an abnormal activity pattern. Identifying anomalies is essential for healthcare management, as this will enable action to avoid prospective problems early and to improve and support residents' ability to live safely and independently in their own homes. Entropy measure analysis is an established method to detect disorder or irregularities in many applications: however, this has rarely been applied in the context of activities of daily living. An experimental evaluation is conducted to detect anomalies obtained from a real home environment. Experimental results are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the entropy measures employed in detecting anomalies in the resident's activity and identifying visiting times in the same environment.
Keywords: activities of daily living; activity recognition; anomaly detection; approximate entropy; behavioural patterns; fuzzy entropy; independent living; multiscale-fuzzy entropy; sample entropy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Chernbumroong S., Cang S., Atkins A., Yu H. Elderly activities recognition and classification for applications in assisted living. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013;40:1662–1674. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.09.004. - DOI
-
- Dini E., Goldring S. Estimating the changing population of the ‘oldest old’. Popul. Trends. 2008;132:8. - PubMed
-
- Subasi A., Khateeb K., Brahimi T., Sarirete A. Innovation in Health Informatics. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. Human activity recognition using machine learning methods in a smart healthcare environment; pp. 123–144.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

