Dental Challenges and the Needs of the Population during the Covid-19 Pandemic Period. Real-Time Surveillance Using Google Trends
- PMID: 33287130
- PMCID: PMC7731122
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17238999
Dental Challenges and the Needs of the Population during the Covid-19 Pandemic Period. Real-Time Surveillance Using Google Trends
Abstract
Background: The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic may lead to changes in the dental needs of the population and new challenges concerning oral health care.
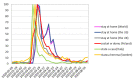
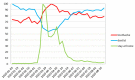
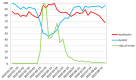
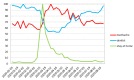
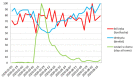
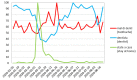
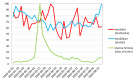
Methods: The Google Trends tool was used to collect data on the Internet search interest. The investigated material was collected from 1 January 2020 to 23 August 2020. Search terms "toothache", "dentist" and "stay at home" were retrieved for the whole world as well as for the US, the UK, Poland, Italy and Sweden.
Results: During the lockdown, correlation analysis indicates the lowest public interest in the word "dentist" one week preceding the peak for "toothache", followed by an increase in the word search for "dentist". On 12 April, worldwide, the maximum of Google Trends Relative Search Volume (RSV) for "toothache" was observed.
Conclusion: Decrease in "dentist" queries during lockdown followed by an increase in "toothache" search predicts greater dental needs in the post-pandemic period. The surveillance shows significant changes in queries for dental-related terms during the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. In order to prepare for future pandemic outbreaks teledentistry programs should be taken into consideration.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; dental treatment needs; oral cancer; oral epidemiology; oral health; oral prevention; teledentistry; toothache.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- James S.L., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cancer Today. [(accessed on 28 August 2020)]; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
-
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. [(accessed on 28 August 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) [(accessed on 22 October 2020)]; Available online: https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous