Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update
- PMID: 33287462
- PMCID: PMC7761826
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9121227
Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update
Abstract
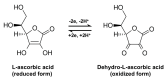
The potential beneficial effects of the antioxidant properties of vitamin C have been investigated in a number of pathological conditions. In this review, we assess both clinical and preclinical studies evaluating the role of vitamin C in cardiac and vascular disorders, including coronary heart disease, heart failure, hypertension, and cerebrovascular diseases. Pitfalls and controversies in investigations on vitamin C and cardiovascular disorders are also discussed.
Keywords: COVID–19; GULO; SVCT; Vitamin C; ascorbic acid; blood pressure; coronavirus; dietary supplements; drug formulations; endothelial dysfunction; heart failure; hypertension; infections; liposomes; oxidative stress; stroke; vascular permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the paper.
Figures
References
-
- De Tullio M.C. Beyond the antioxidant: The double life of vitamin C. Subcell. Biochem. 2012;56:49–65. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical