Acute intracerebral haemorrhage: diagnosis and management
- PMID: 33288539
- PMCID: PMC7982923
- DOI: 10.1136/practneurol-2020-002763
Acute intracerebral haemorrhage: diagnosis and management
Abstract
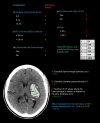
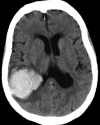
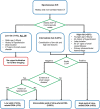
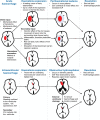
Intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) accounts for half of the disability-adjusted life years lost due to stroke worldwide. Care pathways for acute stroke result in the rapid identification of ICH, but its acute management can prove challenging because no individual treatment has been shown definitively to improve its outcome. Nonetheless, acute stroke unit care improves outcome after ICH, patients benefit from interventions to prevent complications, acute blood pressure lowering appears safe and might have a modest benefit, and implementing a bundle of high-quality acute care is associated with a greater chance of survival. In this article, we address the important questions that neurologists face in the diagnosis and acute management of ICH, and focus on the supporting evidence and practical delivery for the main acute interventions.
Keywords: Stroke; clinical neurology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
