Improved Task-based Functional MRI Language Mapping in Patients with Brain Tumors through Marchenko-Pastur Principal Component Analysis Denoising
- PMID: 33289611
- PMCID: PMC7850264
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020200822
Improved Task-based Functional MRI Language Mapping in Patients with Brain Tumors through Marchenko-Pastur Principal Component Analysis Denoising
Abstract
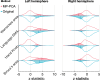
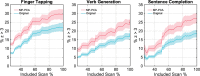
Background Functional MRI improves preoperative planning in patients with brain tumors, but task-correlated signal intensity changes are only 2%-3% above baseline. This makes accurate functional mapping challenging. Marchenko-Pastur principal component analysis (MP-PCA) provides a novel strategy to separate functional MRI signal from noise without requiring user input or prior data representation. Purpose To determine whether MP-PCA denoising improves activation magnitude for task-based functional MRI language mapping in patients with brain tumors. Materials and Methods In this Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act-compliant study, MP-PCA performance was first evaluated by using simulated functional MRI data with a known ground truth. Right-handed, left-language-dominant patients with brain tumors who successfully performed verb generation, sentence completion, and finger tapping functional MRI tasks were retrospectively identified between January 2017 and August 2018. On the group level, for each task, histograms of z scores for original and MP-PCA denoised data were extracted from relevant regions and contralateral homologs were seeded by a neuroradiologist blinded to functional MRI findings. Z scores were compared with paired two-sided t tests, and distributions were compared with effect size measurements and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The number of voxels with a z score greater than 3 was used to measure task sensitivity relative to task duration. Results Twenty-three patients (mean age ± standard deviation, 43 years ± 18; 13 women) were evaluated. MP-PCA denoising led to a higher median z score of task-based functional MRI voxel activation in left hemisphere cortical regions for verb generation (from 3.8 ± 1.0 to 4.5 ± 1.4; P < .001), sentence completion (from 3.7 ± 1.0 to 4.3 ± 1.4; P < .001), and finger tapping (from 6.9 ± 2.4 to 7.9 ± 2.9; P < .001). Median z scores did not improve in contralateral homolog regions for verb generation (from -2.7 ± 0.54 to -2.5 ± 0.40; P = .90), sentence completion (from -2.3 ± 0.21 to -2.4 ± 0.37; P = .39), or finger tapping (from -2.3 ± 1.20 to -2.7 ± 1.40; P = .07). Individual functional MRI task durations could be truncated by at least 40% after MP-PCA without degradation of clinically relevant correlations between functional cortex and functional MRI tasks. Conclusion Denoising with Marchenko-Pastur principal component analysis led to higher task correlations in relevant cortical regions during functional MRI language mapping in patients with brain tumors. © RSNA, 2020 Online supplemental material is available for this article.
Figures

![(a) Plots of functional MRI signal intensity as a function of time (top [without denoising], bottom [with denoising]). We show mean normalized functional MRI signal intensity in the contralateral precentral gyrus hand knob during unilateral finger movements compared with signal intensity after denoising with Marchenko-Pastur principal component analysis (MP-PCA) for one patient. MP-PCA led to decreased random temporal fluctuations in the blood oxygenation level–dependent (BOLD) signal and increased correlation coefficient task model. (b) Plot of temporal correlation function as a function of lag time, f(Δt)/σ2 , of the signal residuals (denoised – original; see Materials and Methods) normalized by the estimated voxelwise noise level shows that residuals have no memory; its mean is zero for all lag times Δt except when Δt = 0, implying that no informative temporal correlations were removed during denoising.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/7c48/7850264/466b504500d5/radiol.2020200822.fig1a.gif)
![(a) Plots of functional MRI signal intensity as a function of time (top [without denoising], bottom [with denoising]). We show mean normalized functional MRI signal intensity in the contralateral precentral gyrus hand knob during unilateral finger movements compared with signal intensity after denoising with Marchenko-Pastur principal component analysis (MP-PCA) for one patient. MP-PCA led to decreased random temporal fluctuations in the blood oxygenation level–dependent (BOLD) signal and increased correlation coefficient task model. (b) Plot of temporal correlation function as a function of lag time, f(Δt)/σ2 , of the signal residuals (denoised – original; see Materials and Methods) normalized by the estimated voxelwise noise level shows that residuals have no memory; its mean is zero for all lag times Δt except when Δt = 0, implying that no informative temporal correlations were removed during denoising.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/7c48/7850264/005f26a07b41/radiol.2020200822.fig1b.gif)


 is a unit Gaussian (a straight black line in the log p(r) vs r2 plot). Histograms of residuals for all methods except MP-PCA exhibit strongly non-Gaussian residuals, indicating the removal of anatomic features. MP-PCA residuals are normally distributed down to an r2 almost equal to 12 (ie, 3.5 standard deviations in the tail of the Gaussian).
is a unit Gaussian (a straight black line in the log p(r) vs r2 plot). Histograms of residuals for all methods except MP-PCA exhibit strongly non-Gaussian residuals, indicating the removal of anatomic features. MP-PCA residuals are normally distributed down to an r2 almost equal to 12 (ie, 3.5 standard deviations in the tail of the Gaussian).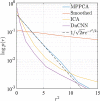
 is a unit Gaussian (a straight black line in the log p(r) vs r2 plot). Histograms of residuals for all methods except MP-PCA exhibit strongly non-Gaussian residuals, indicating the removal of anatomic features. MP-PCA residuals are normally distributed down to an r2 almost equal to 12 (ie, 3.5 standard deviations in the tail of the Gaussian).
is a unit Gaussian (a straight black line in the log p(r) vs r2 plot). Histograms of residuals for all methods except MP-PCA exhibit strongly non-Gaussian residuals, indicating the removal of anatomic features. MP-PCA residuals are normally distributed down to an r2 almost equal to 12 (ie, 3.5 standard deviations in the tail of the Gaussian).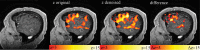
Comment in
-
Wheat from the Chaff: Denoising Functional MRI Data.Radiology. 2021 Apr;299(1):49-50. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210247. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 33595393 No abstract available.
References
-
- Petrella JR, Shah LM, Harris KM, et al. Preoperative functional MR imaging localization of language and motor areas: effect on therapeutic decision making in patients with potentially resectable brain tumors. Radiology 2006;240(3):793–802. - PubMed
-
- Hoult DI, Lauterbur PC. The sensitivity of the zeugmatographic experiment involving human samples. J Magn Reson (1969) 1979;34(2):425–433.
-
- Zacà D, Nickerson JP, Deib G, Pillai JJ. Effectiveness of four different clinical fMRI paradigms for preoperative regional determination of language lateralization in patients with brain tumors. Neuroradiology 2012;54(9):1015–1025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

