MRI quantification techniques in fatty liver: the diagnostic performance of hepatic T1, T2, and stiffness measurements in relation to the proton density fat fraction
- PMID: 33290237
- PMCID: PMC7837725
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2020.19654
MRI quantification techniques in fatty liver: the diagnostic performance of hepatic T1, T2, and stiffness measurements in relation to the proton density fat fraction
Abstract
Purpose: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can progress to liver cirrhosis and is predicted to become the most frequent indication for liver transplantation in the near future. Noninvasive assessment of NAFLD is important for diagnosis and patient management. This study aims to prospectively determine the liver stiffness and T1 and T2 values in patients with NAFLD and to compare the diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and mapping techniques in relation to the proton density fat fraction (PDFF).
Methods: Eighty-three patients with NAFLD and 26 participants with normal livers were imaged with a 1.5 T scanner. PDFF measurements obtained from the multiecho Dixon technique were used to quantify the liver fat. MRE, native T1 mapping (modified Look-Locker inversion recovery [MOLLI] schemes 5(3)3, 3(3)3(3)5, and 3(2)3(2)5 and the B1-corrected variable flip angle [VFA] method), and T2 mapping values were correlated with PDFF. The diagnostic performance of MRE and the mapping techniques were analyzed and compared.
Results: T1 values measured with the MOLLI schemes and the B1-corrected VFA (P < 0.001), and the stiffness values from MRE (P = 0.047) were significantly higher in the NAFLD group. No significant difference was found between the groups in terms of T2 values (P = 0.127). In differentiation of the NAFLD and control groups, the B1-corrected VFA technique had slightly higher accuracy and area under the curve (AUC) than the MOLLI schemes. In the NAFLD group, there was a good correlation between the PDFF, MOLLI 3(3)3(3)5 and 3(2)3(2)5, and VFA T1 measurements (r=0.732; r=0.735; r=0.716, P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: Liver T1 mapping techniques have the potential to distinguish steatotic from nonsteatotic livers, and T1 values seem to have a strong correlation with the liver fat content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
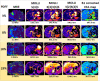
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

