Site-Selective Functionalization of Methionine Residues via Photoredox Catalysis
- PMID: 33290649
- PMCID: PMC8647115
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c09926
Site-Selective Functionalization of Methionine Residues via Photoredox Catalysis
Abstract
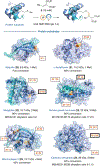
Bioconjugation technologies have revolutionized the practice of biology and medicine by allowing access to novel biomolecular scaffolds. New methods for residue-selective bioconjugation are highly sought to expand the toolbox for a variety of bioconjugation applications. Herein we report a site-selective methionine bioconjugation protocol that uses photoexcited lumiflavin to generate open-shell intermediates. This reduction-potential-gated strategy enables access to residues unavailable with traditional nucleophilicity-based conjugation methods. To demonstrate the versatility and robustness of this new protocol, we have modified various proteins and further utilized this functional handle to append diverse biological payloads.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
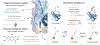


References
-
- Hermanson GT Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA: 2013.
-
-
For selected reviews, see:
Boutureira O; Bernardes GJL Advances in Chemical Protein Modification. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2174. Stephanopoulos N; Francis MB Choosing an Effective Protein Bioconjugation Strategy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 876. Schumacher D; Hackenberger CP R More than Add-on: Chemoselective Reactions for the Synthesis of Functional Peptides and Proteins. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 22, 62. deGruyter JN; Malins LR; Baran PS Residue-Specific Peptide Modification: A Chemist’s Guide. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 3863.
-
-
- Chen X; Muthoosamy K; Pfisterer A; Neumann B; Weil T Site-Selective Lysine Modification of Native Proteins and Peptides via Kinetically Controlled Labeling. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 500. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y; Ho SO; Gassman NR; Korlann Y; Landorf EV; Collart FR; Weiss S Efficient Site-Specific Labeling of Proteins via Cysteines. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 786. - PMC - PubMed
- Smith MEB; Schumacher FF; Ryan CP; Tedaldi LM; Papaioannou D; Waksman G; Caddick S; Baker JR Protein Modification, Bioconjugation, and Disulfide Bridging Using Bromomaleimides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1960. - PMC - PubMed
- Morales-Sanffutos J; Lopez-Jaramillo FJ; Hernandez-Mateo F; Santoyo-Gonzalez F Vinyl Sulfone Bifunctional Tag Reagents for Single-Point Modification of Proteins. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 4039. - PubMed
-
- Gavrilyuk J; Ban H; Nagano M; Hakamata W; Barbas CF III Formylbenzene Diazonium Hexafluorophosphate Reagent for Tyrosine-Selective Modification of Proteins and the Introduction of a Bioorthogonal Aldehyde. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 2321. - PMC - PubMed
- Zhang J; Ma D; Du D; Xi Z; Yi L An Efficient Reagent for Covalent Introduction of Alkynes into Proteins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 9528. - PubMed
- Joshi NS; Whitaker LR; Francis MBA Three Component Mannich-Type Reaction for Selective Tyrosine Bioconjugation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15942. - PubMed
- Mileo E; Etienne E; Martinho M; Lebrun R; Roubaud V; Tordo P; Gontero B; Guigliarelli B; Marque SRA; Belle V Enlarging the Panoply of Site-Directed Spin Labeling Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (SDSL-EPR): Sensitive and Selective Spin-Labeling of Tyrosine Using an Isoindoline-Based Nitroxide. Bioconjugate Chem. 2013, 24, 1110. - PubMed
- Guo H-M; Minakawa M; Ueno L; Tanaka F Synthesis and Evaluation of a Cyclic Imine Derivative Conjugated to a Fluorescent Molecule for Labeling of Proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1210. - PMC - PubMed
- Ban H, Gavrilyuk J; Barbas CF III Tyrosine Bioconjugation through Aqueous Ene-Type Reactions: A Click Like Reaction for Tyrosine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

