Exploring the Multifaceted Therapeutic Potential of Withaferin A and Its Derivatives
- PMID: 33291236
- PMCID: PMC7762146
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8120571
Exploring the Multifaceted Therapeutic Potential of Withaferin A and Its Derivatives
Abstract
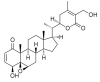
Withaferin A (WA), a manifold studied, C28-steroidal lactone withanolide found in Withania somnifera. Given its unique beneficial effects, it has gathered attention in the era of modern science. Cancer, being considered a "hopeless case and the leading cause of death worldwide, and the available conventional therapies have many lacunae in the form of side effects. The poly pharmaceutical natural compound, WA treatment, displayed attenuation of various cancer hallmarks by altering oxidative stress, promoting apoptosis, and autophagy, inhibiting cell proliferation, reducing angiogenesis, and metastasis progression. The cellular proteins associated with antitumor pathways were also discussed. WA structural modifications attack multiple signal transduction pathways and enhance the therapeutic outcomes in various diseases. Moreover, it has shown validated pharmacological effects against multiple neurodegenerative diseases by inhibiting acetylcholesterinases and butyrylcholinesterases enzyme activity, antidiabetic activity by upregulating adiponectin and preventing the phosphorylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARγ), cardioprotective activity by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and suppressing mitochondrial apoptosis. The current review is an extensive survey of various WA associated disease targets, its pharmacokinetics, synergistic combination, modifications, and biological activities.
Keywords: Withaferin A; anticancer; autophagy; chaperone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating anticancer properties of Withaferin A-a potent phytochemical.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 19;13:975320. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.975320. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the NEMO/IKKβ association complex formation, a novel mechanism associated with the NF-κB activation suppression by Withania somnifera's key metabolite withaferin A.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 2;11 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S4-S25. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143809 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic characterization of Withaferin A-targeted protein networks for the treatment of monoclonal myeloma gammopathies.J Proteomics. 2018 May 15;179:17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29448055
-
The Therapeutic Effects of Withaferin A against Cancer: Overview and Updates.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(4):404-418. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230418094708. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37076466 Review.
-
Overview of the anticancer activity of withaferin A, an active constituent of the Indian ginseng Withania somnifera.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jul;27(21):26025-26035. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09028-0. Epub 2020 May 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32405942 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Coronavirus Disease 2019 on the Quality of Associated Care in Patients with Gastric Cancer.Middle East J Dig Dis. 2024 Jan;16(1):12-22. doi: 10.34172/mejdd.2024.363. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2024. PMID: 39050096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Human Colorectal Cancer Using RNASeq Data Validated on the Molecular Level with Real-Time PCR.Biochem Genet. 2024 Aug;62(4):3260-3284. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10593-5. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38097858 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Elderberry Snack Bars: A Sensory, Nutritional, and Rheological Evaluation.Foods. 2023 Sep 23;12(19):3544. doi: 10.3390/foods12193544. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37835197 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating anticancer properties of Withaferin A-a potent phytochemical.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 19;13:975320. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.975320. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of propolis on membrane bound enzymes linked with breast cancer.Bioinformation. 2022 Dec 31;18(12):1192-1195. doi: 10.6026/973206300181192. eCollection 2022. Bioinformation. 2022. PMID: 37701506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- John J. Therapeutic potential of Withania somnifera: A report on phytopharmacological properties. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014;5:2131–2148.
-
- Lemma M.T., Ahmed A.M., Elhady M.T., Ngo H.T., Vu T.L.H., Sang T.K., Campos-Alberto E., Sayed A., Mizukami S., Na-Bangchang K. Medicinal plants for in vitro antiplasmodial activities: A systematic review of literature. Parasitol. Int. 2017:66713–66720. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources