Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples
- PMID: 33291257
- PMCID: PMC7762187
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10121056
Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples
Abstract
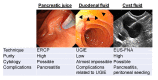
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Most patients with PDAC present with symptomatic, surgically unresectable disease. Therefore, the establishment of strategies for the early detection is urgently needed. Molecular biomarkers might be useful in various phases of a strategy to identify high-risk individuals in the general population and to detect high-risk lesions during intense surveillance programs combined with imaging modalities. However, the low sensitivity and specificity of biomarkers currently available for PDAC, such as carbohydrate 19-9 (CA19-9), contribute to the late diagnosis of this deadly disease. Although almost all classes of biomarker assays have been studied, most of them are used in the context of symptomatic diseases. Compared to other body fluids, pancreatic juice and duodenal fluid are better sources of DNA, RNA, proteins, and exosomes derived from neoplastic cells and have the potential to increase the sensitivity/specificity of these biomarkers. The number of studies using duodenal fluid with or without secretin stimulation for DNA/protein marker tests have been increasing because of the less-invasiveness in comparison to pancreatic juice collection by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA). Genomic analyses have been very well-studied, and based on PDAC progression model, mutations detected in pancreatic juice/duodenal fluid seem to indicate the presence of microscopic precursors and high-grade dysplasia/invasive cancer. In addition to known proteins overexpressed both in precursors and PDACs, such as CEA and S100P, comprehensive proteomic analysis of pancreatic juice from patients with PDAC identified many proteins which were not previously described. A novel technique to isolate exosomes from pancreatic juice was recently invented and identification of exosomal microRNA's 21 and 155 could be biomarkers for diagnosis of PDAC. Since many studies have explored biomarkers in fluid samples containing pancreatic juice and reported excellent diagnostic accuracy, we need to discuss how these biomarker assays can be validated and utilized in the strategy of early detection of PDAC.
Keywords: duodenal juice/fluid; pancreatic cancer; pancreatic juice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of pancreatic juice cytology by using synthetic secretin in the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Dig Endosc. 2018 Nov;30(6):771-776. doi: 10.1111/den.13203. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Dig Endosc. 2018. PMID: 29873113
-
Pancreatic Juice Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2019 Jul;26(7):2104-2111. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07269-z. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30820789
-
A minimally invasive and simple screening test for detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using biomarkers in duodenal juice.Pancreas. 2013 Mar;42(2):187-92. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182649979. Pancreas. 2013. PMID: 23407480
-
Updates and Critical Evaluation on Novel Biomarkers for the Malignant Progression of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas.Anticancer Res. 2017 May;37(5):2185-2194. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11553. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28476781 Review.
-
Early screening and diagnosis strategies of pancreatic cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Dec;41(12):1257-1274. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12204. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34331845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of PLEXIND1/TGFβ Signaling Axis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Progression Correlates with the Mutational Status of KRAS.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 11;13(16):4048. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164048. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439202 Free PMC article.
-
QN-302 demonstrates opposing effects between i-motif and G-quadruplex DNA structures in the promoter of the S100P gene.Org Biomol Chem. 2023 Dec 20;22(1):55-58. doi: 10.1039/d3ob01464a. Org Biomol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37970888 Free PMC article.
-
TSPAN4+ fibroblasts coordinate metastatic niche assembly through migrasome-driven metabolic reprogramming and stromal-immune crosstalk in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 May 15;16:1594879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1594879. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40443671 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies DCBLD2 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 23;8:659168. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.659168. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33834039 Free PMC article.
-
Actin gamma 1 is a critical regulator of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2022 May-Jun;28(3):239-246. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_356_21. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 34856725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cotton P.B., Cremer M., Robberecht P., Christophe J. Proceedings: Biochemical studies on pure pancreatic juice obtained by duodenoscopic cannulation of the pancreatic duct in conscious patients. Gut. 1974;15:838. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

