Analysis of Animal Well-Being When Supplementing Drinking Water with Tramadol or Metamizole during Chronic Pancreatitis
- PMID: 33291366
- PMCID: PMC7762076
- DOI: 10.3390/ani10122306
Analysis of Animal Well-Being When Supplementing Drinking Water with Tramadol or Metamizole during Chronic Pancreatitis
Abstract
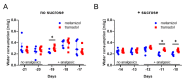
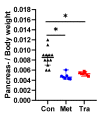
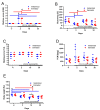
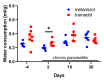
Pain management during in vivo experiments is an animal welfare concern and is in many countries also legally required. In this study, we evaluated C57Bl/6J mice when 3 g/L metamizole or 1 g/L tramadol was provided via drinking water, before and during cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis. Supplementation of drinking water with metamizole or tramadol did not significantly reduce the amount of consumed water. In order to evaluate the wellbeing of mice, a distress score, burrowing activity, nesting behavior, and body weight was assessed. Before induction of pancreatitis, neither tramadol nor metamizole influenced these readout parameters. Chronic pancreatitis caused a significantly increased distress score, decreased burrowing activity and a reduction in body weight. Mice drinking tramadol-supplemented water experienced less loss in body weight and consumed more water than mice drinking metamizole, at a few time-points during chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatic atrophy, a characteristic feature of chronic pancreatitis was not differentially influenced by either analgesic. In conclusion, both analgesics can be used during 33 days of chronic pancreatitis, but tramadol seems to be moderately advantageous when compared to metamizole.
Keywords: analgesia; rodents; sweetened water; wellbeing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- European Union Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. [(accessed on 25 September 2020)]; Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32010L0063....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

