Proof of Concept Study for Increasing Tenascin-C-Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumors Previously Subjected to Therapy: X-Irradiation Increases Tumor Uptake
- PMID: 33291427
- PMCID: PMC7762098
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123652
Proof of Concept Study for Increasing Tenascin-C-Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumors Previously Subjected to Therapy: X-Irradiation Increases Tumor Uptake
Abstract
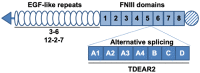
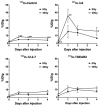
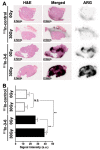
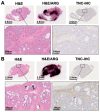
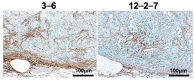
In treatment-refractory cancers, tumor tissues damaged by therapy initiate the repair response; therefore, tumor tissues must be exposed to an additional burden before successful repair. We hypothesized that an agent recognizing a molecule that responds to anticancer treatment-induced tissue injury could deliver an additional antitumor agent including a radionuclide to damaged cancer tissues during repair. We selected the extracellular matrix glycoprotein tenascin-C (TNC) as such a molecule, and three antibodies recognizing human and murine TNC were employed to evaluate X-irradiation-induced changes in TNC uptake by subcutaneous tumors. TNC expression was assessed by immunohistochemical staining of BxPC-3 tumors treated with or without X-irradiation (30 Gy) for 7 days. Antibodies against TNC (3-6, 12-2-7, TDEAR) and a control antibody were radiolabeled with 111In and injected into nude mice having BxPC-3 tumors 7 days after X-irradiation, and temporal uptake was monitored for an additional 4 days by biodistribution and single-photon emission computed tomography with computed tomography (SPECT/CT) studies. Intratumoral distribution was analyzed by autoradiography. The immunohistochemical signal for TNC expression was faint in nontreated tumors but increased and expanded with time until day 7 after X-irradiation. Biodistribution studies revealed increased tumor uptake of all three 111In-labeled antibodies and the control antibody. However, a statistically significant increase in uptake was evident only for 111In-labeled 3-6 (35% injected dose (ID)/g for 30 Gy vs. 15% ID/g for 0 Gy at day 1, p < 0.01), whereas limited changes in 111In-labeled TDEAR2, 12-2-27, and control antibody were observed (several % ID/g for 0 and 30 Gy). Serial SPECT/CT imaging with 111In-labeled 3-6 or control antibody provided consistent results. Autoradiography revealed noticeably stronger signals in irradiated tumors injected with 111In-labeled 3-6 compared with each of the nonirradiated tumors and the control antibody. The signals were observed in TNC-expressing stroma. Markedly increased uptake of 111In-labeled 3-6 in irradiated tumors supports our concept that an agent, such as an antibody, that recognizes a molecule involved in tissue injury repair, such as TNC, could enhance drug delivery to tumor tissues that have undergone therapy. The combination of antibody 3-6 coupled to a tumoricidal drug and conventional therapy has the potential to achieve better outcomes for patients with refractory cancer.
Keywords: cancer stroma; injured tissue; radioisotope; tissue remodeling; treatment resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
M.K. holds stocks of Matrix Cell Research Institute Inc. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


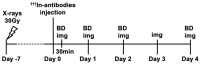

Similar articles
-
Dynamic expression of tenascin-C after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion: assessment by 125I-anti-tenascin-C antibody imaging.J Nucl Med. 2010 Jul;51(7):1116-22. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.071340. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Nucl Med. 2010. PMID: 20554738
-
Successful Inflammation Imaging of Non-Human Primate Hearts Using an Antibody Specific for Tenascin-C.Int Heart J. 2019 Jan 25;60(1):151-158. doi: 10.1536/ihj.17-734. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Int Heart J. 2019. PMID: 30464121
-
Effect of postconditioning on dynamic expression of tenascin-C and left ventricular remodeling after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion.EJNMMI Res. 2015 Apr 2;5:21. doi: 10.1186/s13550-015-0100-8. eCollection 2015. EJNMMI Res. 2015. PMID: 25883880 Free PMC article.
-
Tenascin-C Function in Glioma: Immunomodulation and Beyond.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1272:149-172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-48457-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32845507 Review.
-
Clinical advances in TNC delivery vectors and their conjugate agents.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Jan;253:108577. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108577. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38081519 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Tenascin-C on Radiotherapy in a Novel Syngeneic Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Model With Spontaneous Dissemination to the Lymph Nodes.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 5;12:636108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636108. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34290694 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Radiolabelled Derivatives of R954 for Detection of Bradykinin B1 Receptor in Cancer Cells: Studies on Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 7;17(7):902. doi: 10.3390/ph17070902. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065752 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Strategies to Address Critical Challenges in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;14(17):4115. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174115. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077652 Free PMC article.
-
The natural sulfoglycolipid derivative SQAP improves the therapeutic efficacy of tissue factor-targeted radioimmunotherapy in the stroma-rich pancreatic cancer model BxPC-3.Transl Oncol. 2022 Jan;15(1):101285. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101285. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34839108 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Tenascin-C are Clinical Biomarkers and Improve Tumor-Derived DNA Analysis in Glioblastoma Patients.ACS Nano. 2025 Mar 18;19(10):9844-9859. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c13599. Epub 2025 Mar 8. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40056466 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

