Non-Coding RNAs as Mediators of Epigenetic Changes in Malignancies
- PMID: 33291485
- PMCID: PMC7762117
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123657
Non-Coding RNAs as Mediators of Epigenetic Changes in Malignancies
Abstract
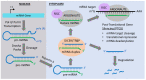
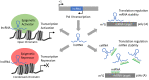
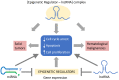
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are untranslated RNA molecules that regulate gene expressions. NcRNAs include small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), transfer RNAs (tRNAs), circular RNAs (cRNAs) and piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). This review focuses on two types of ncRNAs: microRNAs (miRNAs) or short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). We highlight the mechanisms by which miRNAs and lncRNAs impact the epigenome in the context of cancer. Both miRNAs and lncRNAs have the ability to interact with numerous epigenetic modifiers and transcription factors to influence gene expression. The aberrant expression of these ncRNAs is associated with the development and progression of tumors. The primary reason for their deregulated expression can be attributed to epigenetic alterations. Epigenetic alterations can cause the misregulation of ncRNAs. The experimental evidence indicated that most abnormally expressed ncRNAs impact cellular proliferation and apoptotic pathways, and such changes are cancer-dependent. In vitro and in vivo experiments show that, depending on the cancer type, either the upregulation or downregulation of ncRNAs can prevent the proliferation and progression of cancer. Therefore, a better understanding on how ncRNAs impact tumorigenesis could serve to develop new therapeutic treatments. Here, we review the involvement of ncRNAs in cancer epigenetics and highlight their use in clinical therapy.
Keywords: cancer; epigenetics; lncRNAs; miRNAs; ncRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

